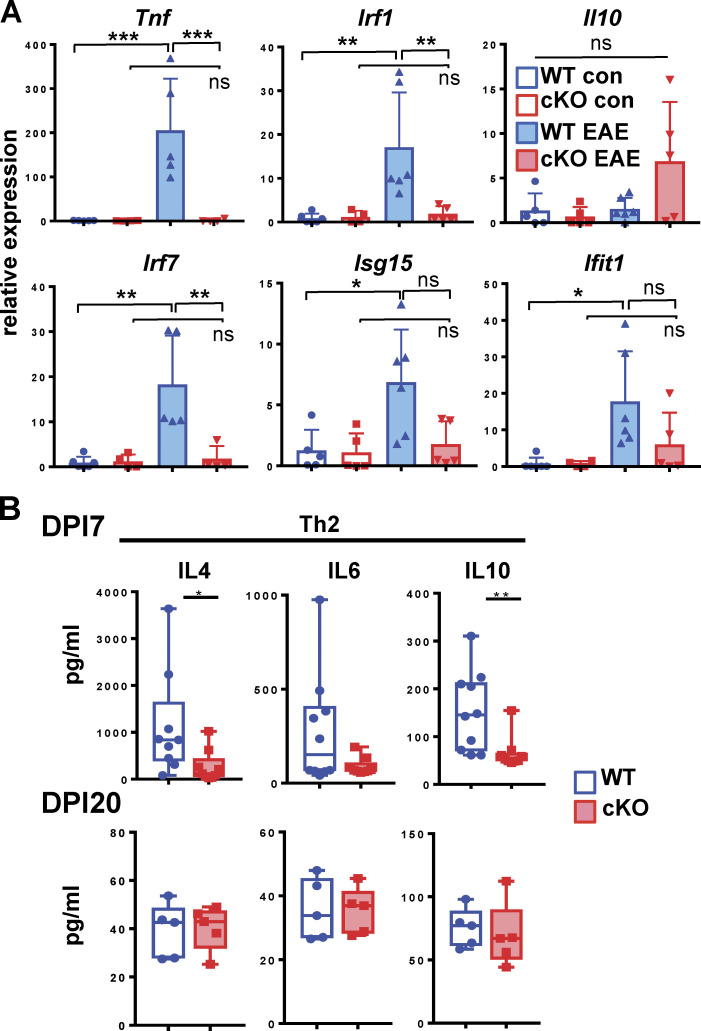
Figure S3.
GRIP1-cKO mice develop less spinal cord inflammation and attenuated early peripheral Th2 T cell response in vitro. (A) Spinal cords were harvested from control (WT = 6; GRIP1-cKO = 5) and EAE DPI20 (WT = 6; GRIP1 cKO = 6) mice, and total RNA was extracted. Relative expression of the indicated genes was evaluated by RT-qPCR, normalized to that of the Actb housekeeping gene, and expressed relative to WT control (=1; two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.005. ns, nonsignificant. (B) Spleens were collected at DPI7 (WT = 10; GRIP1-cKO = 9; two independent experiments) and DPI20 (n = 5 each from one experiment). CD4+ T cells were isolated, then restimulated with MOG35–55 in vitro, and the indicated Th2-secreted cytokines were quantified using CBA (unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.