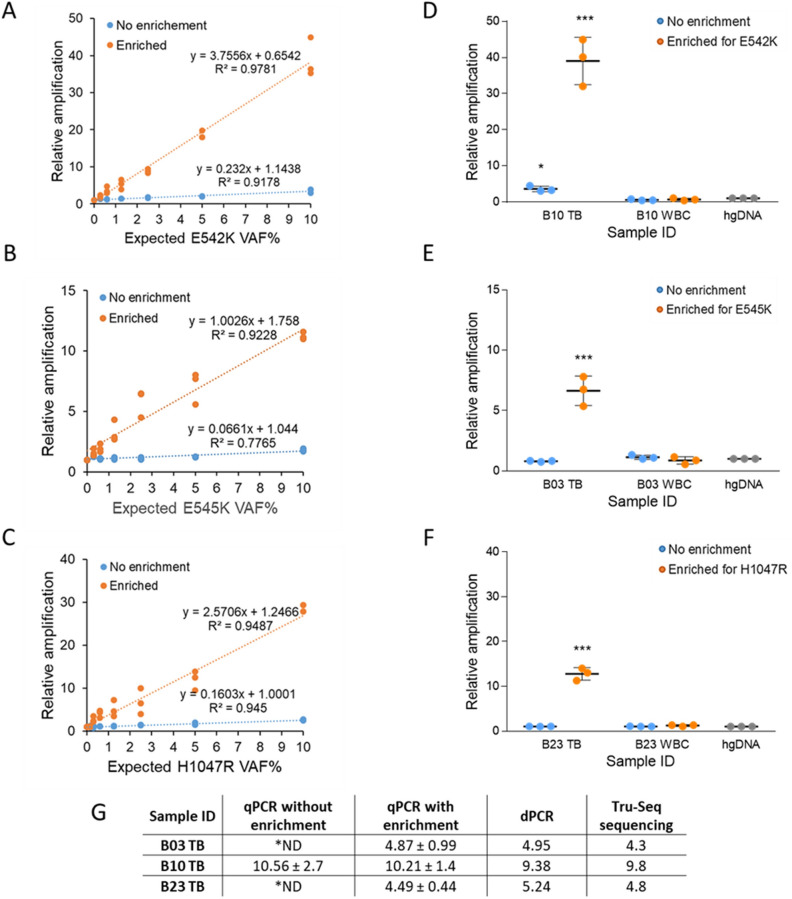
Figure 2.
NaME-PrO wild type sequence elimination and mutant allele detection by SYBR Green qPCR. Genomic DNA from cell lines containing PIK3CA E542K (A), E545K (B), and H1047R (C) mutations were serially diluted in wild type DNA with decreasing mutation abundances. Mutation detection was performed in enriched samples and matched untreated controls by SYBR Green qPCR including a wild type blocking primer. A linear regression equation was estimated for data points for each mutation. PIK3CA mutation enrichment and detection assays (D) E542K, (E) E545K, (F) H1047R were applied to low mutation abundance tissue biopsies (TB) and white blood cell (WBC) control samples. Data was analysed by a ΔΔCt method, in which relative amplification was calculated relative to WT human genomic DNA (hgDNA), and shown as mean mutant fold amplification ± SD. Due to a limited enrichment reaction volume (10 µl), all qPCR points were obtained in duplicates in three independent experiments (n = 3). ***P < 0.001 compared with PIK3CA WT, *P < 0.05 compared with PIK3CA WT (Student’s t test). (G) Linear regression was applied to calculate the initial variant allele fraction for every tissue biopsy sample in qPCR experiments, and compared to dPCR and Tru-Seq panel sequencing results. *ND—no meaningful result, due to VAF < LOD.