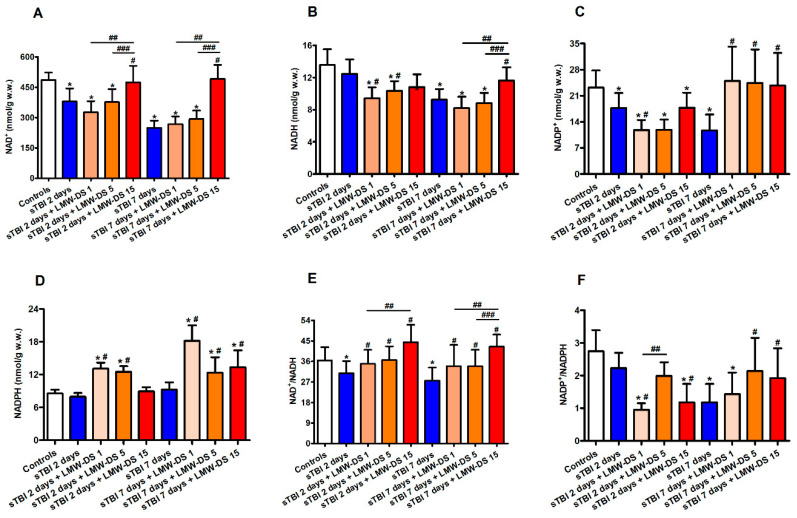
Figure 5.
Effect of subcutaneous injection of increasing doses of LMW-DS (ILB®) on the cerebral concentrations of NAD+ (A), NADH (B), NADP+ (C), and NADPH (D), and of the NAD+/NADH (E) and NADP+/NADPH (F) ratios as valuable indicators of oxido-reductive metabolism of the nervous cell energy state. The parameters of interest were determined by HPLC on deproteinized cerebral homogenates at 2 and 7 days post-impact, both in untreated sTBI rats (TBI 2 days and TBI 7 days) and in rats receiving 1, 5, or 15 mg/kg b.w. LMW-DS (ILB®) administered 30 min after sTBI. Controls are represented by sham-operated rats. Values are the mean ± SD of 12 different animals and are expressed as nmol/g w.w. * Significantly different from sham-operated control rats, p < 0.05. # Significantly different from the corresponding time point of untreated sTBI rats, p < 0.05. ## Significantly different from LMW-DS 1, p < 0.05. ### Significantly different from LMW-DS 5, p < 0.05.