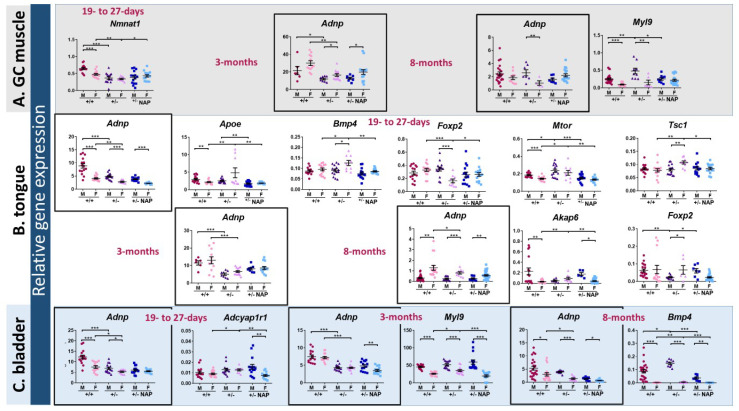
Figure 1.
Activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (Adnp) haploinsufficiency alters muscle (GC muscle (A), tongue (B) and bladder (C)) gene expression in a sex- and age-dependent manner: NAP amelioration. Total RNA was extracted from 3 groups of age youngest group: 19–27-day-old mice (males: Adnp+/+ n = 5, Adnp+/– n = 5, Adnp+/+ NAP n = 4, Adnp+/– NAP n = 5; females: Adnp+/+ n = 5, Adnp+/– n = 3, Adnp+/+ NAP n = 4, Adnp+/– NAP n = 5). Young adults: 3-month-old mice (for muscle and tongue tissues males: Adnp+/+ n = 3, Adnp+/– n = 4, Adnp+/+ NAP n = 4, Adnp+/– NAP n = 4; females: Adnp+/+ n = 6, Adnp+/– n = 7, Adnp+/+ NAP n = 6, Adnp+/– NAP n = 8/9, respectively. For bladder of both sexes: Adnp+/+ n = 5, Adnp+/– n = 5, Adnp+/+ NAP n = 5, Adnp+/– NAP n = 5). Old group: 8-month-old mice (males: Adnp+/+ n = 8, Adnp+/– n = 3, Adnp+/+ NAP n = 4, Adnp+/– NAP n = 3; females: Adnp+/+ n = 6, Adnp+/– n = 3, Adnp+/+ NAP n = 5, Adnp+/– NAP n = 10/11 (in bladder and tongue n = 11)). Results were normalized to Hprt. The comparative Ct method was implemented here (2−ΔCT) for quantification of transcripts (indicated as relative gene expression and further explained in the Methods). A two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test revealed significant differences between vehicle-treated Adnp+/+ and Adnp+/– mice and between NAP and vehicle-treated Adnp+/– mice (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001). Sex differences were determined by an unpaired Student’s t-test.