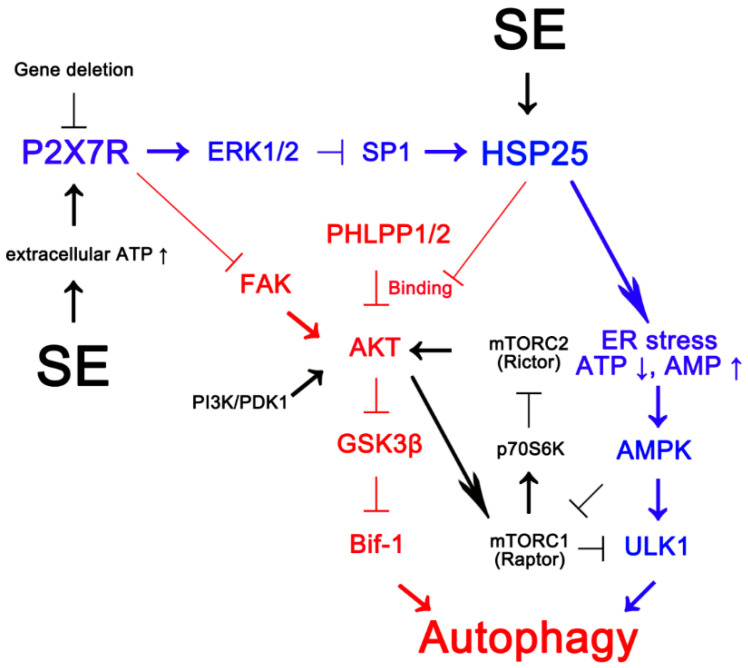
Figure 10.
Scheme of inhibitory role of P2X7R in AKT-S473 hyperphosphorylation during astroglial autophagy induced by KA injection based on the present data (red) and previous reports (blue and black) [6,14,21,22,23]. After KA injection, P2X7R activation inhibits FAK phosphorylation and HSP25 transactivation via ERK1/2-mediated SP1-T739 phosphorylation. P2X7R deletion leads to sustained HSP25 expression, which activates AMPK/ULK1-mediated astroglial autophagy (blue) [6]. In addition, P2X7R deletion increases FAK autophosphorylation [20]. Subsequently, the activated FAK phosphorylates AKT, and the prolonged HSP25 expression abrogates the binding of PHLPP1/2 to AKT, which result in AKT-S473 hyperphosphorylation. Sustained AKT-S473 phosphorylation exerts AKT/GSK3β-mediated Bif-1 induction that triggers astroglial autophagy (red), independent of PI3K/PDK1 and mTOR complex (mTORC) 1/2 activities (black). Thus, these findings suggest that P2X7R may be a fine-tuner of autophagic process in astrocytes by regulating AKT-S473 phosphorylation.