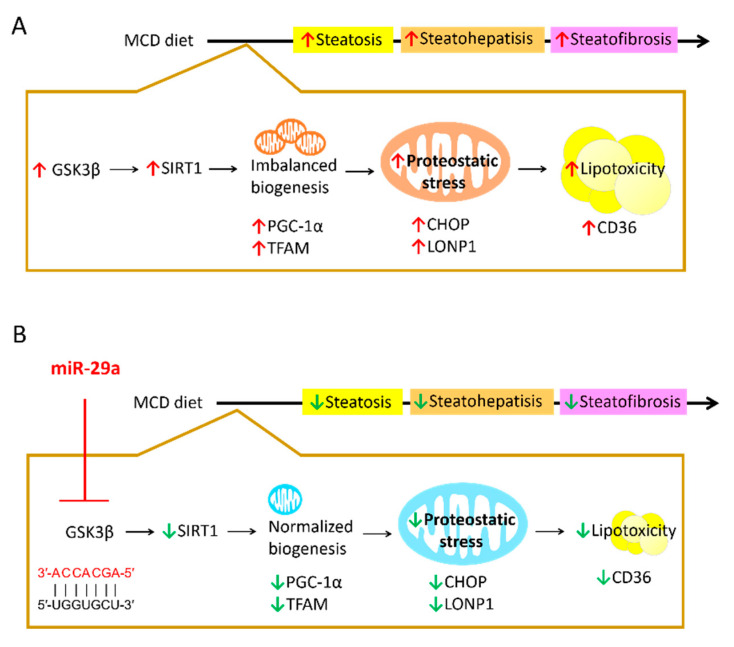
Figure 7.
Proposed model of the miR-29a-relayed pathway in the prevention of diet-induced hepatic injury. (A) MCD diet leads to an increase in GSK3β, which induces imbalanced mitochondrial biogenesis mediated by SIRT1. As such, protein folding workload in mitochondria can stimulate proteostatic stress, leading to mitochondrial malfunction and subsequent hepatic lipid accumulation. Increased hepatic lipotoxicity can contribute to the progression of steatosis, steatohepatitis and steatofibrosis. (B) miR-29a can suppress GSK3β expression by direct binding to its 3′UTR to reverse the aberrant SIRT1-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis and mitochondrial proteostatic stress, ultimately mitigating the pathological progression. Red arrow: increase; Green arrow: decrease.