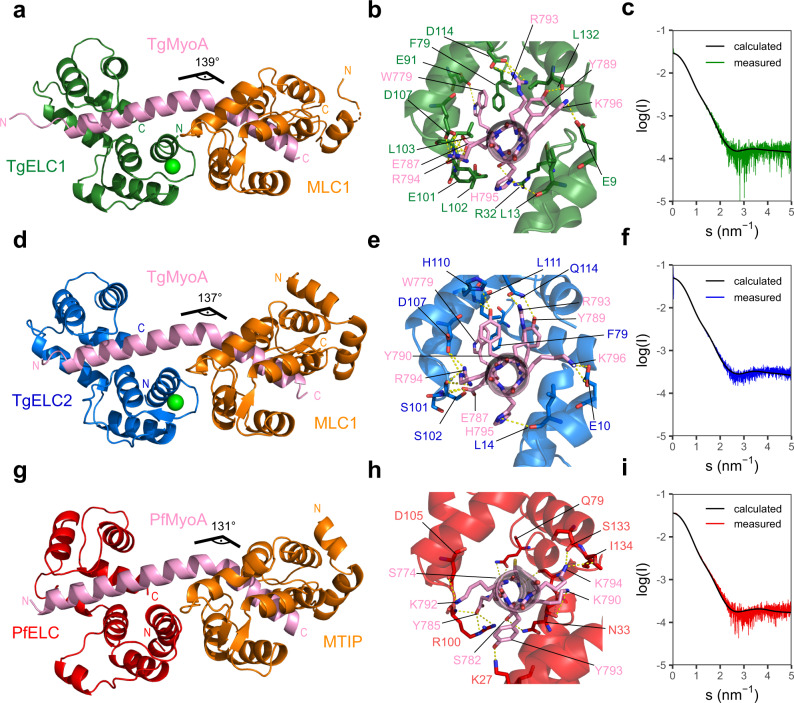
Fig. 4. X-ray structures of trimeric glideosome sub-complexes.
a, d, g Crystal structures of trimeric complex of TgELC1 (green) or TgELC2 (blue) or PfELC (red) with MyoA-C (pink) and MLC1/MTIP (orange). The complexes are topologically similar and the MyoA helix displays a characteristic kink between residues 801–803. ELCs bind upstream of the MLC1/MTIP binding site. b, e, h Binding interface between MyoA-C (pink) and TgELC1 (green) in complex 1, TgELC2 (blue) in complex 2 or PfELC (red) in P. falciparum complex. Residues involved in polar interactions are labeled with the corresponding color and shown in stick representation. Most polar interactions are mediated by the C-terminal lobes of ELCs and the hydrophobic interactions between ELCs and the conserved hydrophobic MyoA residues play a crucial role in complex formation as evident from ITC measurements. c, f, i SAXS analysis of the trimeric complexes. Calculated scattering curves of complex 1, complex 2 and P. falciparum complex fit the respective experimental data with χ2 equal to 1.26, 2.41 and 3.9, respectively.