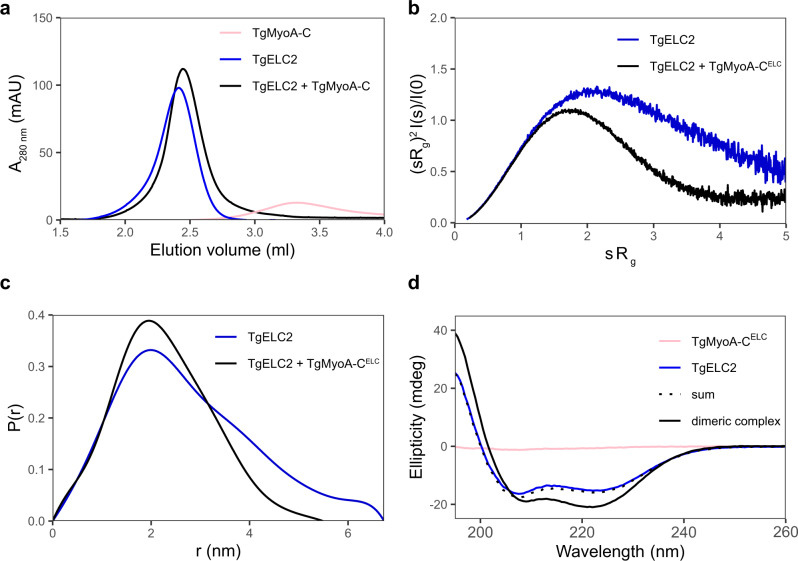
Fig. 5. TgELCs and TgMyoA undergo large conformational changes upon binding.
a Dimeric complex of TgELC2 and TgMyoA-C elutes at longer retention times than isolated TgELC2 on Superdex 200 5/150 column, suggesting that the hydrodynamic radius of TgELC2 decreases upon TgMyoA-C binding. b Dimensionless Kratky plots of isolated TgELC2 and in complex with TgMyoA-C. The plot of TgELC2 in complex with TgMyoA-CELC (black) has a maximum close to sRg = √3 and converges to zero, unlike isolated TgELC2 (blue), suggesting that TgELC2 in isolation is rather extended and compacts upon binding to TgMyoA. c The distance distribution calculated by Guinier analysis from the SAXS data further confirms that TgELC2 undergoes compaction upon TgMyoA binding. TgELC2 displays wider distance distribution with dmax = 6.7 nm, whereas the distance distribution of the dimeric complex is narrower with dmax = 5.5 nm. d The far-UV CD data indicate that TgELC2 induces a α-helical structure in TgMyoA upon binding. The individual spectra of TgELC2 and TgMyoA-CELC do not sum up to the CD spectrum of their dimeric complex and the CD spectrum of the dimeric complex displays more pronounced features of α-helical secondary structure with lower ellipticity at 222 nm and higher ellipticity at 195 nm compared to the sum of individual components. CD spectra were recorded in a 1 mm cuvette at a concentration of 5 μM of each component in 10 mM NaP (pH 7.5), 150 mM NaF and 0.25 mM TCEP at 20 °C.