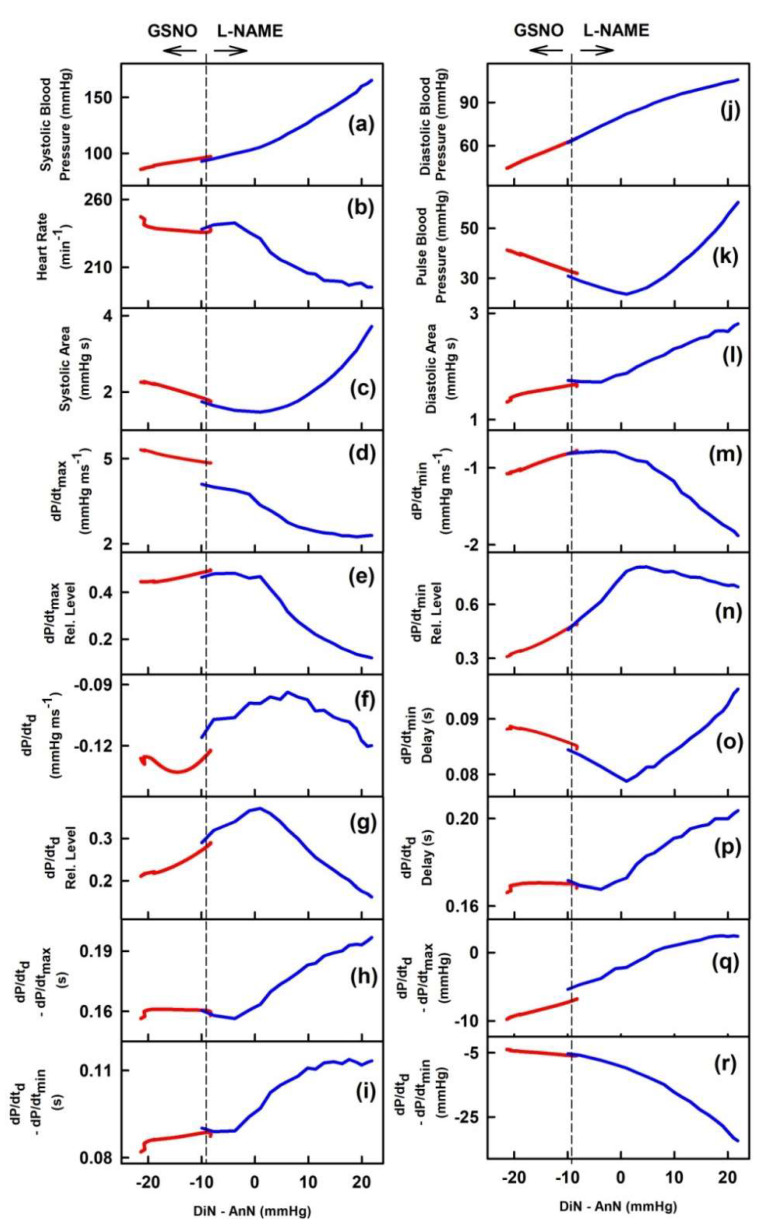
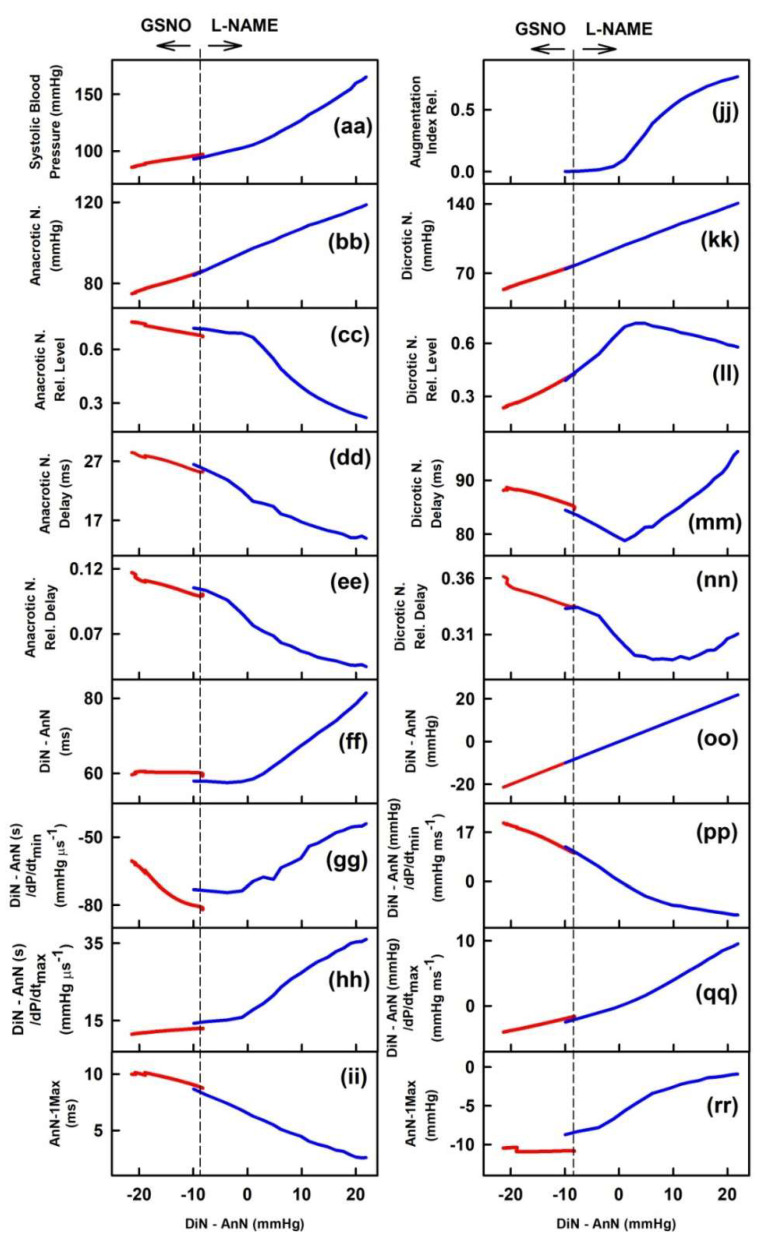
Figure 6.
Two-dimensional cross-relationships of DiN-AnN pressure difference (in mmHg) to 34 rat HPs for conditions of increased/decreased NO bioavailability. The increase of NO bioavailability was caused by i.v. administration of 32 nmol·kg−1 GSNO (red line; average from 10 experiments; data calculated from Figure 6 published in [22]). Red line was calculated from the time segment during which BP decreased after GSNO administration. The decrease of NO bioavailability after i.v. administration of 25 mg·kg−1 l-NAME (blue line; average from six experiments; data calculated from Figure 3 published in [23]) is shown. Blue line was calculated from the time segment during which BP increased after l-NAME administration. Arrows indicate the time direction after GSNO and l-NAME administration.