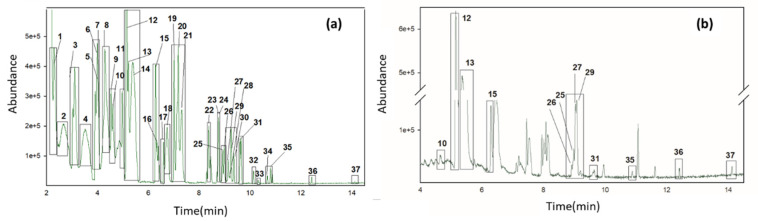
Figure 1.
Total ion chromatogram (TIC) of a standards mixture (a) and an extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) sample (b) showing the volatile compounds identified by headspace gas chromatography (HS-GC) coupled with mass spectrometry (MS): (1) ethyl acetate, (2) 2-butanone, (3) 2-pentanone, (4) 1-penten-3-one, (5) 2-methyl-1-butanol, (6) 3-methyl-1-butanol, (7) 4-methyl-pentan-2-one, (8) trans-2-pentenal, (9) 1-pentanol, (10) cis-2-penten-1-ol, (11) 2-hexanone, (12) n-octane, (13) hexanal, (14) ethyl butyrate, (15) trans-2-hexen-1-al, (16) ethyl isovalerate, (17) 1-hexanol, (18) trans-2-hexen-1-ol, (19) 2-heptanone, (20) propyl butyrate, (21) heptanal, (22) trans-2-heptenal, (23) 1-octen-3-one, (24) 1-octen-3-ol, (25) 6-methyl-5-hepten-2-one, (26) 2-octanone, (27) 2-octanol, (28) octanal, (29) 3-hexenyl-acetate, (30) hexyl acetate, (31) limonene, (32) trans-2-octenal, (33) 1-octanol, (34) 2-nonanone, (35) nonanal, (36) decanal, (37) trans-2-decenal, (38) diethyl phthalate.