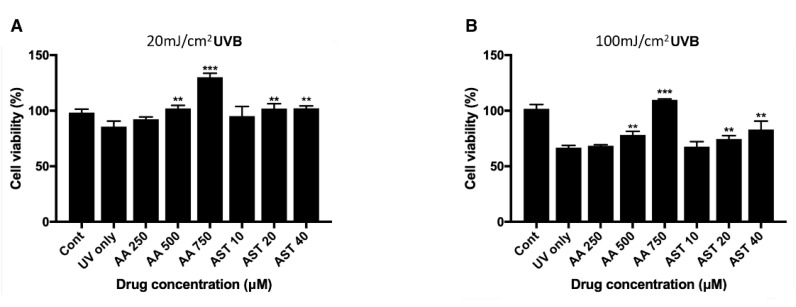
Figure 5.
Effect of ascorbic acid and astaxanthin on UVB-induced oxidative stress model of ARPE-19. The effect of various concentration of ascorbic acid and astaxanthin (pretreated for 6 h and additional 24 h after UVB irradiation) on the response of ARPE-19 cells to sublethal dose of 20 mJ/cm2 (A) or lethal dose of 100 mJ/cm2 UVB (B). The cell viability was determined by MTT assay 24 h after the irradiation. Treatment of ascorbic acid (500–750 μM) and astaxanthin (20–40 μM) significantly increased ARPE-19 cell viability following 20 mJ/cm2 UVB irradiation (A). Ascorbic acid (500–750 μM) and astaxanthin (20–40 μM) also significantly increased the cell viability after 100 mJ/cm2 UVB irradiation (B). Asterisks indicate a significant increment in cell viability compared with cells treated with UVB only (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001). UVB, ultraviolet B; AA, ascorbic acid; AST, astaxanthin; MTT, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide.