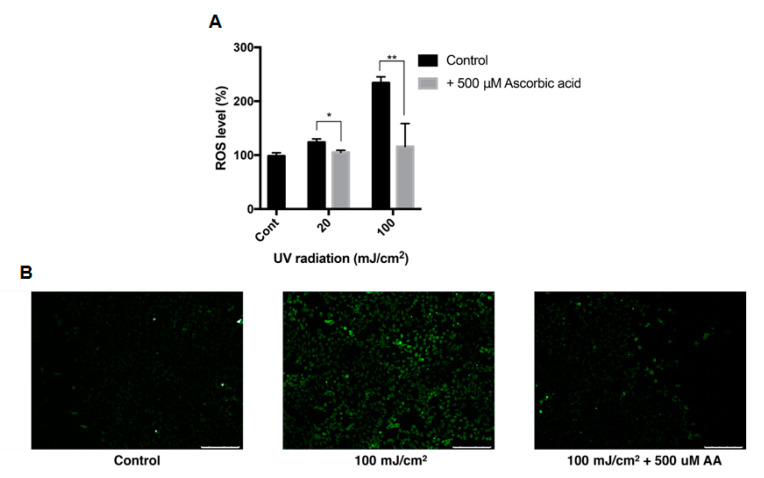
Figure 6.
Intracellular ROS level of ARPE-19 after UVB treatment with ascorbic acid. The effects of ascorbic acid on the intracellular ROS level of ARPE-19 under UVB-induced oxidative stress were examined by DCFH-DA assay. Ascorbic acid at 500 μM significantly reduced the ROS level after UVB irradiation (20–100 mJ/cm2) compared to groups with UVB irradiation only (A). The green fluorescence of the reacted DCFH-DA which indicates the ROS level, was observed with fluorescence microscopy (scale bar 250 μm) (B). Asterisks indicate a significant reduction in ROS level compared with control cells only with UVB exposure without ascorbic acid treatment (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01). ROS, reactive oxygen species; UVB, ultraviolet B; DCFH-DA, 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate; AA, ascorbic acid.