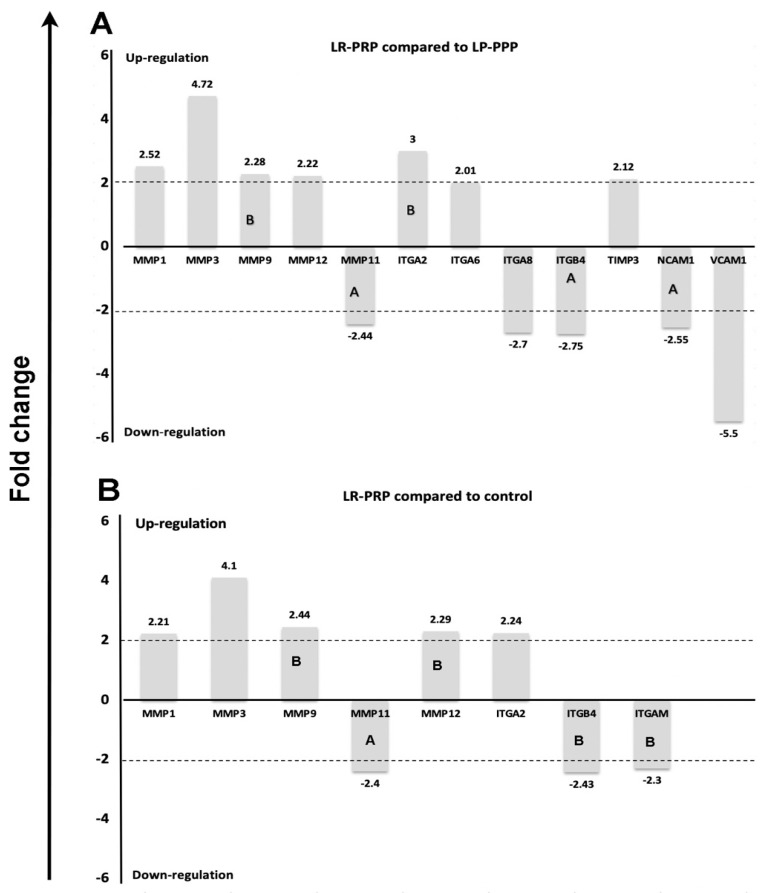
Figure 3.
The human extracellular matrix and adhesion molecules RT2 Profiler PCR gene array. Fibroblasts supplemented with (A) LR-PRP versus LP-PPP (control) at 12 h or (B) LR-PRP versus serum-free media (negative control) representing significant up- and down-regulated genes (more than two-fold) and those with no significant change (less than two-fold). Abbreviations: MMP1, matrix metallopeptidase 1 (collagenase); MMP3, matrix metallopeptidase 3 (stromelysin); MMP9, matrix metallopeptidase 9 (gelatinase); MMP11, matrix metallopeptidase 11 (stromelysin); MMP12, matrix metallopeptidase 12 (metalloelastase); ITGA2, integrin alpha 2; ITGA6, integrin, alpha 6; ITGA8, integrin alpha 8; ITGAM, integrin alpha M chain; ITGB4, integrin beta 4; TIMP3, metalloproteinase inhibitor 3; NCAM1, neural cell adhesion molecule 1; VCAM1, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, leucocyte-rich—platelet-rich plasma (LR-PRP), leucocyte-poor—platelet poor plasma (LP-PPP). Letter A specifies that the gene’s average threshold cycle is relatively high (>30) in either the control or the test sample and is reasonably low in the other sample (<30). These data mean that the gene’s expression is relatively low in one sample and reasonably detected in the other sample, which suggests that the actual fold-change value is at least as large as the calculated and reported fold-change result. Letter B specifies that the gene’s average threshold cycle is relatively high (>30), meaning that its relative expression level is low, in both control and test samples, and the p value for the fold-change is either unavailable or relatively high (p > 0.05).