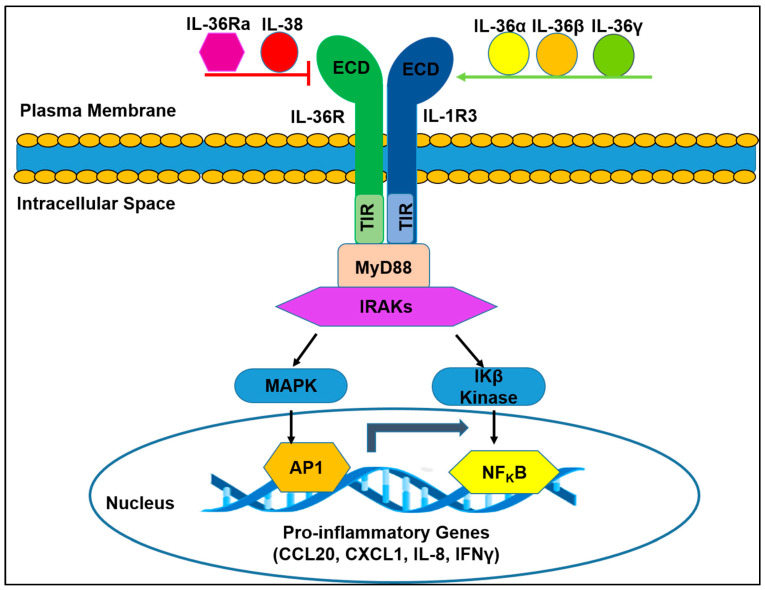
Figure 1.
Structural and molecular depiction of interleukin 36 receptor (IL-36R) signaling cascade. Upon binding to its agonists (IL-36α, IL-36β, or IL-36γ), IL-36R heterdimerizes with its co-receptor IL-1R3 (IL-1RAcP). The formation of the IL-36R/IL-36/IL-1R3 complex results in the recruitment of MyD88 and IRAKs, which subsequently activates the MAPK and NFKB pathways. Activation of MAPK results in the transcription of inflammatory genes regulated by AP-1, while the phosphorylation of IKβα (a negative regulator of NFKB) by Ikβ kinase leads to the translocation of NFKB to the nucleus, which aids in the transcription of genes important for mediating inflammation. The IL-36R mediated activation of pro-inflammatory gene expression can be inhibited by IL-36Ra or IL-38. Extracellular domain (ECD), toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain (TIR), myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88), interleukin-1 receptor associated kinases like 1 and 2 (IRAKs), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), activator protein-1 (AP-1), NF-Kappa-B Inhibitor Alpha (IKβα), and nuclear factor kappa light chain enhancer of activated B cells (NFKB), CCl, C-C motif chemokine ligand; CXCL, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand; IFN, interferon.