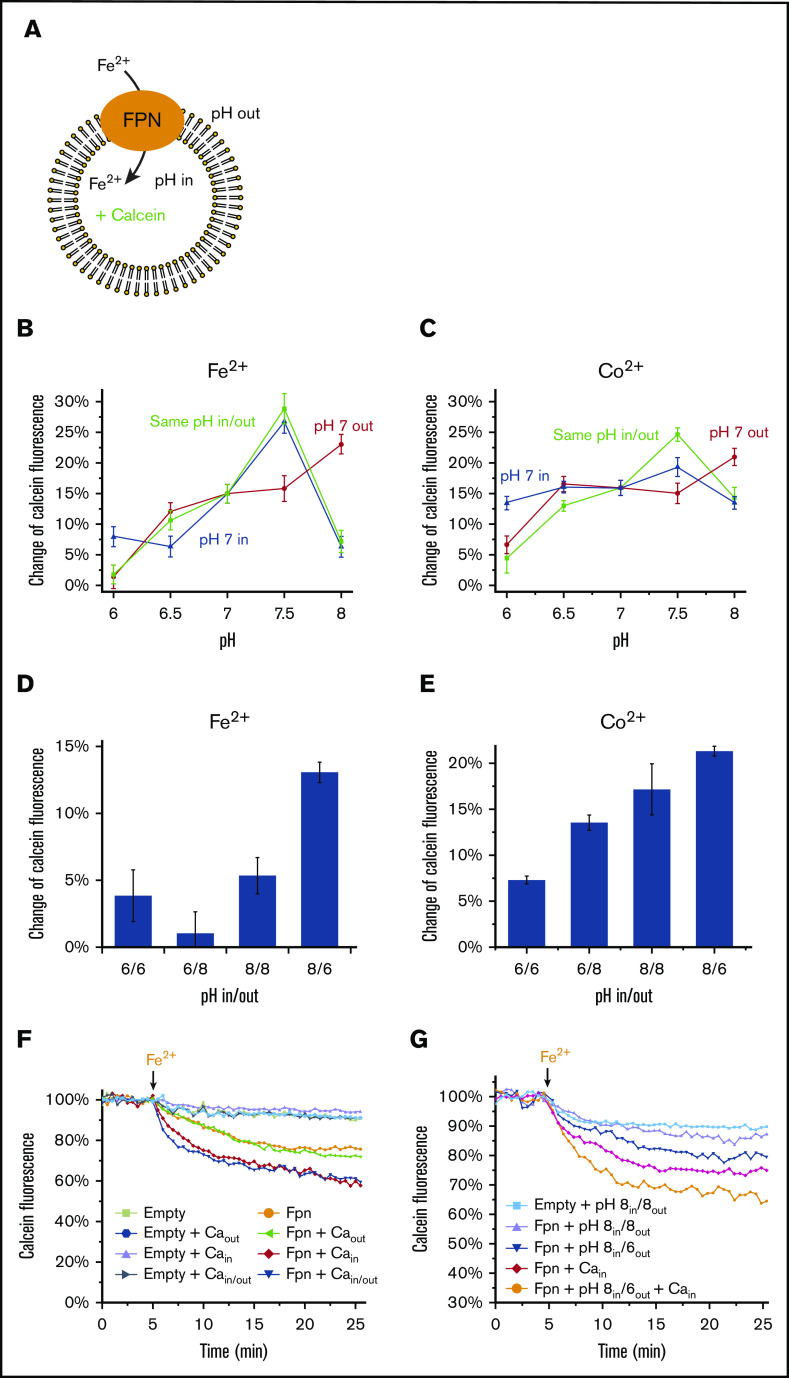
Figure 3.
Proton gradients facilitate Fe2+and Co2+transport in the same direction. (A) Assay of the Fe2+ transport activity (same as in Figure 1) with the variations of pH inside and outside the liposome. (B) Comparison of the pH profiles of Fe2+ transport with and without proton gradients. The same pHs inside and outside the liposomes (green curve) show the pH dependence of ferroportin (FPN) activity without a proton gradient. The proton gradients across the membrane are generated by keeping pH 7 at inside (blue curve) or outside (red curve) the liposomes and varying the pHs at the other side. Fe2+ is provided at 10 μM concentration. (C) Comparison of the pH profiles of Co2+ transport with and without proton gradients. Co2+ is provided at 100 μM concentration. (D-E) Relative Fe2+ and Co2+ transport activities with proton gradients between pH 6 and pH 8. All error bars are standard deviations from 3 repeats. (F) Fe2+ transport activities with 5 mM Ca2+ inside and/or outside the liposomes. (G) Fe2+ transport activities with 5 mM Ca2+ inside and with proton gradients between pH 6 and pH 8.