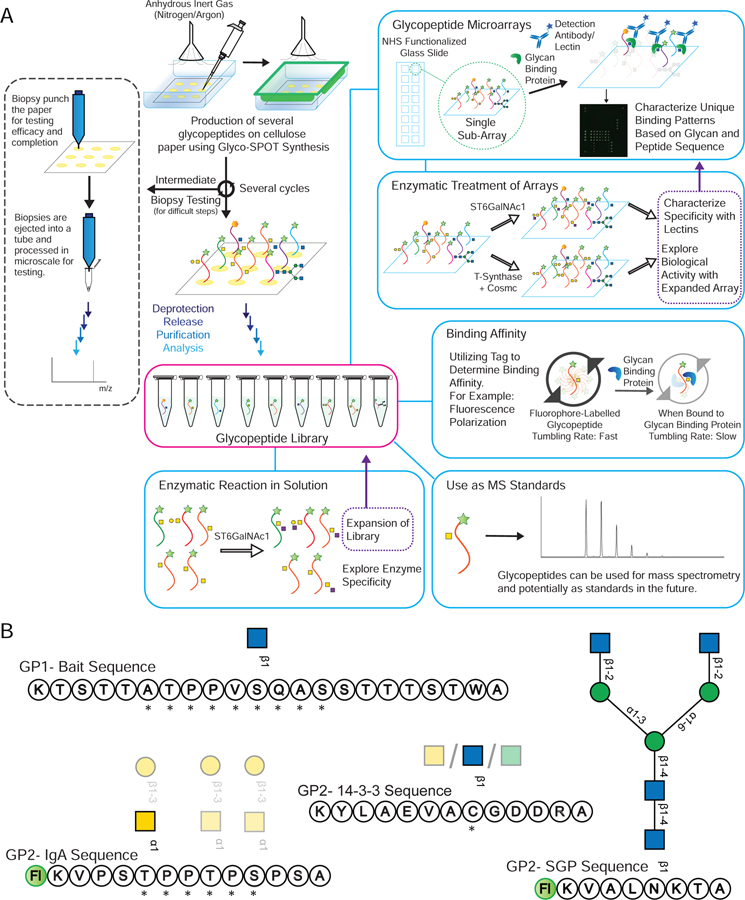
Figure 2.
(A) An overview of Glyco-SPOT synthesis strategy and its applications. Briefly, the spot synthesis is carried out on a piece of cellulose filter paper in an enclosed container under a flow of nitrogen using the setup shown above. During the several synthesis cycles, biopsy testing of the spots can be carried out as shown the on the left panel to check the efficacy and completeness of the reaction (See also Figure S1). After all the cycles are complete, the glycopeptide side chains are deprotected, the glycopeptides are released, purified and characterized using analytical techniques such as HPLC and MALDI-MS. For comparison of Glyco-SPOT synthesis strategy to traditional peptide library synthesis strategies see also Table S5. These glycopeptides can then be utilized for a number of applications: (a) The glycopeptides synthesized can further be treated with glycosyltransferase enzymes to either expand the structures in the library, or to explore the enzymatic specificity. (b) To print glycopeptide microarrays that can be utilized to probe glycan binding protein interactions. (c) Such glycopeptide microarrays can also be treated with enzymes, and be probed with lectins to probe the specificity of enzymes or to use such modified microarrays to probe binding of other proteins. (d) Using appropriate tags one can also utilize the glycopeptides to measure binding affinity. (e) The glycopeptides synthesized using this technique have been characterized using LC-MS and can potentially be used as standards in future experiments. (B) Example set of glycopeptides synthesized. The prototypical sequences of a series are shown, along with * indicating variations of amino acid sequences made for the peptides or translucent glycan symbols showing the different glycoforms synthesized.  indicates 5(6)-carboxyfluorescein on the N-terminus. For complete list of sequences see also Tables S1 and S2.
indicates 5(6)-carboxyfluorescein on the N-terminus. For complete list of sequences see also Tables S1 and S2.