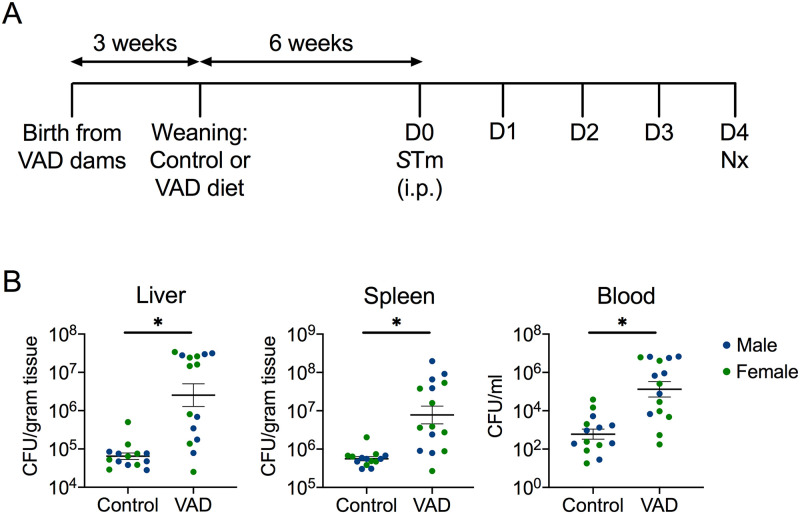
Fig 1. Systemic burden of Salmonella is higher in vitamin A-deficient mice.
To generate vitamin A-deficient (VAD) mice, C57BL/6 Slc11a1+/+ pregnant mice were put on a VAD diet 2 weeks into gestation (A). At 3 weeks, pups were weaned onto either a VAD or control diet. Male (n = 7) and female (n = 7–8) mice on each diet were infected with S. Typhimurium (STm) D23580 via the intraperitoneal (i.p.) route at 9 weeks of age and systemic bacterial burden was characterized by colony-forming units (CFU) in liver, spleen and blood collected at necropsy (Nx) 4 days after infection (B). Data represent mean ± SEM. Significance between control and VAD mice was determined with a Mann-Whitney test of log-transformed values. A p<0.05 was considered significant.