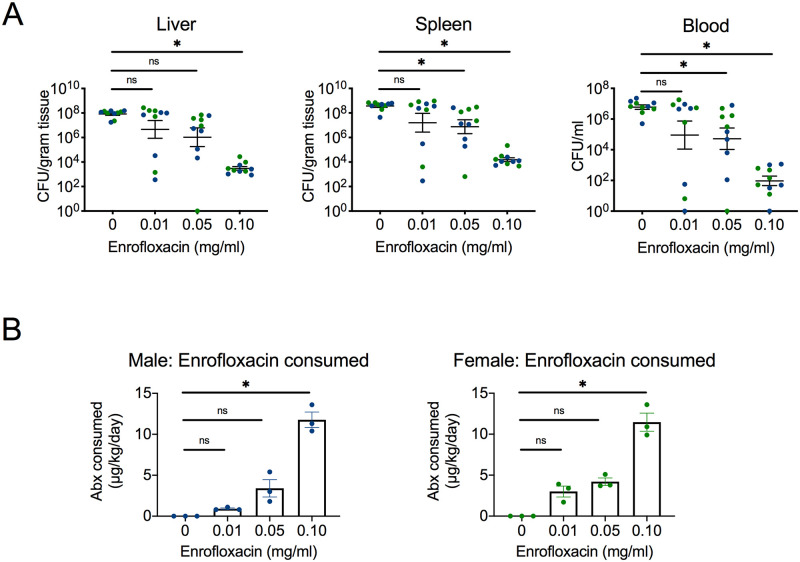
Fig 4. Antibiotic treatment failure occurs at specific concentrations in vivo.
Enrofloxacin was administered directly into the drinking water on day 2 post-infection with multidrug-resistant S. Typhimurium D23580. Groups of C57BL/6J male (n = 5) and female (n = 5) mice on a standard diet were assessed for the following treatment groups: 0 mg/ml, 0.01 mg/ml, 0.05 mg/ml, and 0.10 mg/ml. Systemic bacterial burden was characterized by CFU in liver, spleen and blood collected at necropsy 5 days after infection (A). Water weights and mouse weights were collected daily. The average enrofloxacin consumed (μg/kg/day) was determined for each group based on water and mouse weights for days 2–3, 3–4 and 4–5 (B). Data are reported as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined on log-transformed values (A) or calculated values (B) with a Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn’s multiple comparisons test (*, p<0.05; ns, not significant).