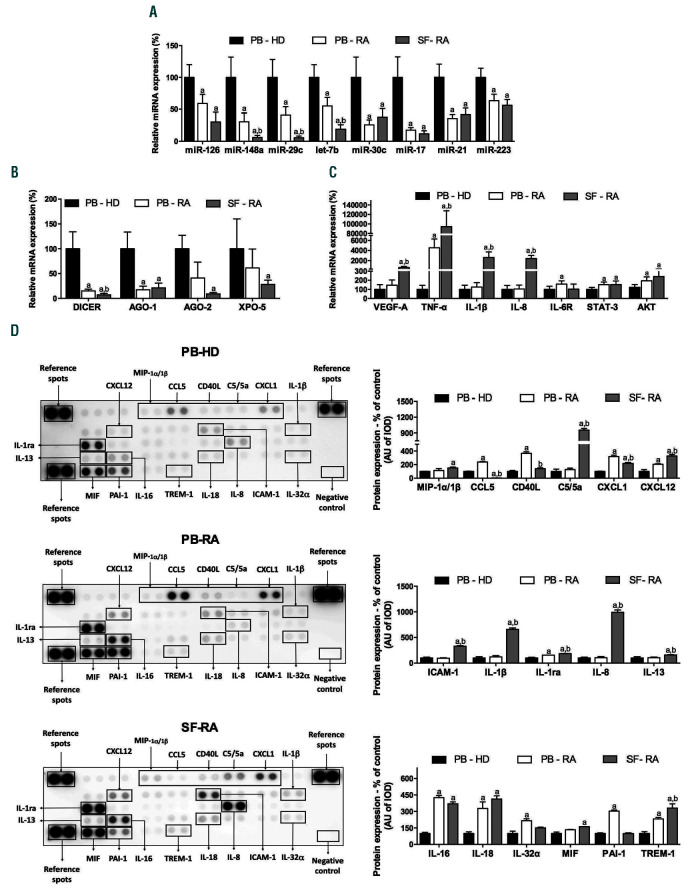
Figure 3.
Low abundance of miRNA levels in rheumatoid arthritis neutrophils might be due to a defect in the miRNA processing. (A) Validation of the miRNA array in PB-HD neutrophils (n=40), PB-RA neutrophils (n=40) and SF-RA neutrophils (n=40). (B) Expression of genes related to miRNA biogenesis machinery in PB-HD (n=40), PB-RA (n=40) and SF-RA neutrophils (n=40). (C) Gene expression of putative mRNA targets of the selected miRNA in PB-HD (n=40), PB-RA (n=40) and SFRA neutrophils (n=40). (D) Proteome profile of chemokines and cytokines in neutrophils from PB-HD (n=10), PB-RA (n=10) and SF-RA neutrophils (n=10). MiR: microRNA; RA: rheumatoid arthritis; PB: peripheral blood; HD: healthy donor; SF: synovial fluid; AGO-1: argonaute-1; AGO-2: argonaute-2; XPO-5: exportin-5; VEGF-A: vascular endothelial growth factor A; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IL-1β: interleukin-1 beta; IL-8: interleukin-8; IL-6R: interleukin-6 receptor; STAT-3: signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; AKT: protein kinase B; MIP-1a/1β: macrophage inflammatory protein 1 alpha/1 beta; CCL5: chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5; CD40 ligand: cluster differentiation 40 ligand; C5/5a: complement component C5/5a; CXCL-1: chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1; CXCL12: chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 12; ICAM-1: intercellular adhesion molecule 1; IL-1ra: interleukin-1 receptor antagonist; IL-13: interleukin 13; IL-16: interleukin 16; IL-18: interleukin 18; IL-32a: interleukin 32 alpha; MIF: macrophage migration inhibitory factor; PAI-1: plasminogen activator inhibitor-type 1; TREM-1: triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM); a: significant differences vs. PB-HD P<0.05; b: significant differences vs. PB-RA P<0.05.