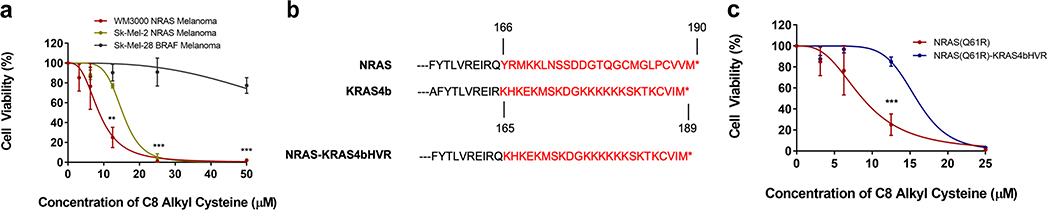
Figure 4.
C8 Alkyl Cysteine Preferentially Reduces Cell Viability in NRAS-Driven versus BRAF-Driven Melanoma. (a) A WST-1 assay was used to assess the cell viability of NRAS-mutated melanoma cell lines (WM3000 and Sk-Mel-2) vs. a BRAF-mutated melanoma cell line (Sk-Mel-28) after 24-hour incubation with increasing concentrations of C8 alkyl cysteine. Results are the mean ± s.d. of three independent experiments. Each row (concentration) was analyzed individually, without assuming a consistent SD. **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001 (multiple t-tests). (b) The last 24 amino acids of the hypervariable region (HVR) of NRAS and KRAS4b are marked in red. The final protein construct of the NRAS-KRAS4bHVR fusion that was used for experimentation is at the bottom. (c) A WST-1 assay was used to assess the cell viability of the original WM3000 NRAS-mutated melanoma cell line and the WM3000 NRAS-mutated melanoma cell line with KRAS4b HVR replacing the original NRAS C-terminal HVR. Both cell lines were treated with increasing concentrations of C8 alkyl cysteine for 24 hours. Results are the mean ± s.d. of three independent experiments. Each row (concentration) was analyzed individually, without assuming a consistent SD. ***p ≤ 0.001 (multiple t-tests).