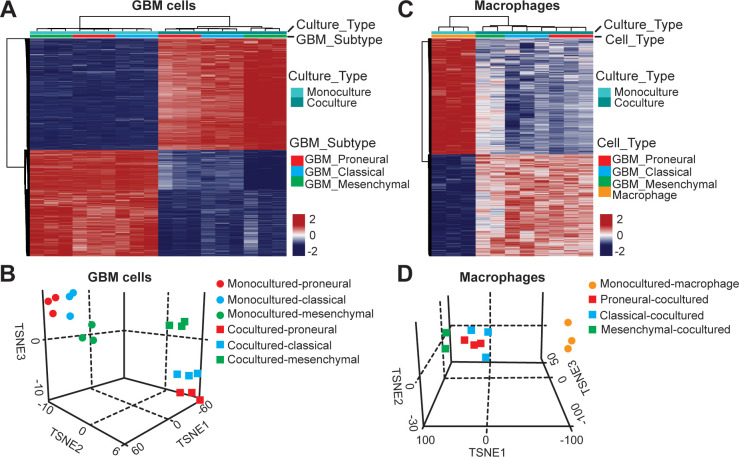
Figure 4. DNA methylation analysis of interactions between patient-derived GBM cell and macrophage in an engineered 3D GBM niche environment.
(A) Whole genome DNA methylation analysis showing top 10,000 differentially methylated probes of patient-derived PN (GBML20), CL (GBML08) and MES (GBML91) GBM cells cultured in a 3D brain-mimicking ECM environment with or without macrophages. (B) tSNE analysis of mono-cultured and co-cultured GBM cells showing clear separation of all molecular GBM subtypes, PN (GBML20), CL (GBML08) and MES (GBML91) (each in triplicate) in the same direction when exposed to macrophages. However, the effect appears to be different in the three molecular subtypes with PN GBM mostly affected by presence of macrophage. (C) Whole genome DNA methylation analysis showing top 10,000 differentially methylated probes of mono-cultured and GBM cell-educated macrophages. (D) tSNE analysis of mono-cultured and patient-derived GBM cell-educated macrophages showing distinct shifts in methylation in all molecular GBM subtypes. However, MES GBM cell co-cultured macrophages cluster showed a more distinct separation.
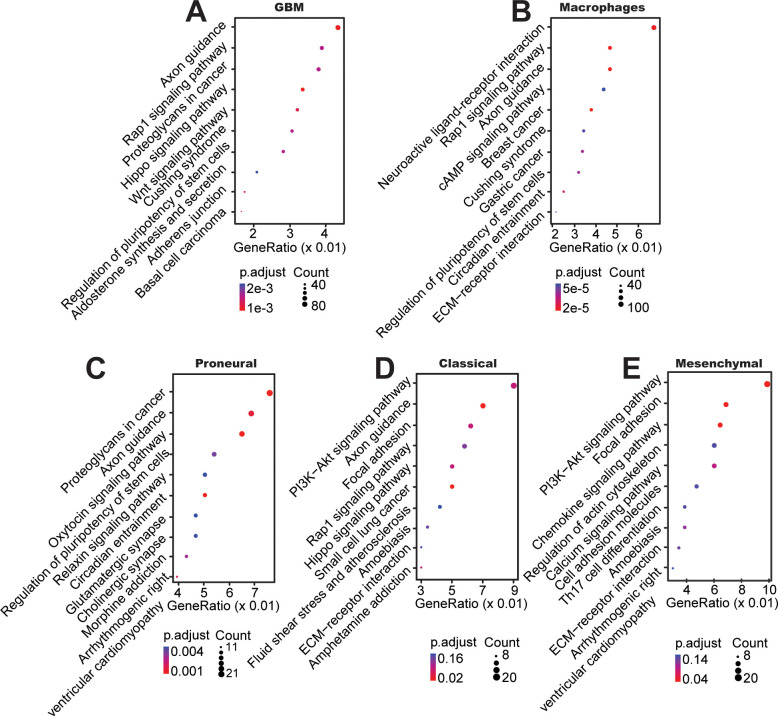
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Top KEGG pathways between mono-cultured and co-cultured GBM cells in a 3D brain-mimicking ECM environment.
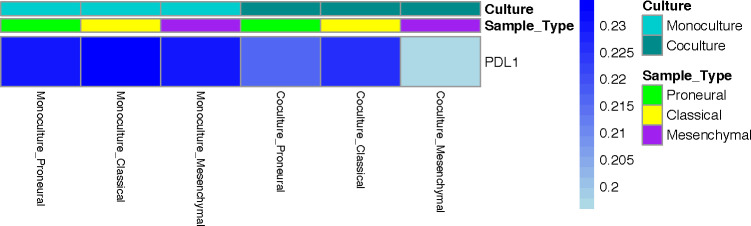
Figure 4—figure supplement 2. PD-L1 promoter methylation in mono-cultured and co-cultured GBM cells in a 3D brain-mimicking ECM environment.
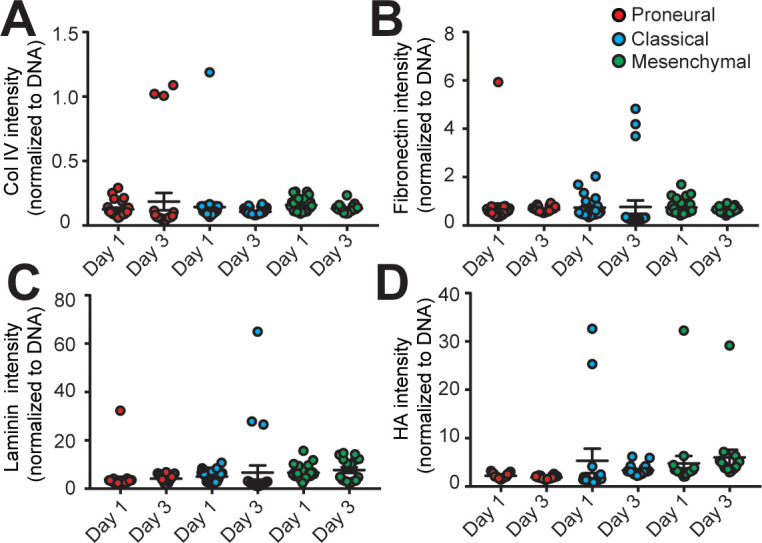
Figure 4—figure supplement 3. Analysis of extracellular matrix composition in different engineered GBM niches.