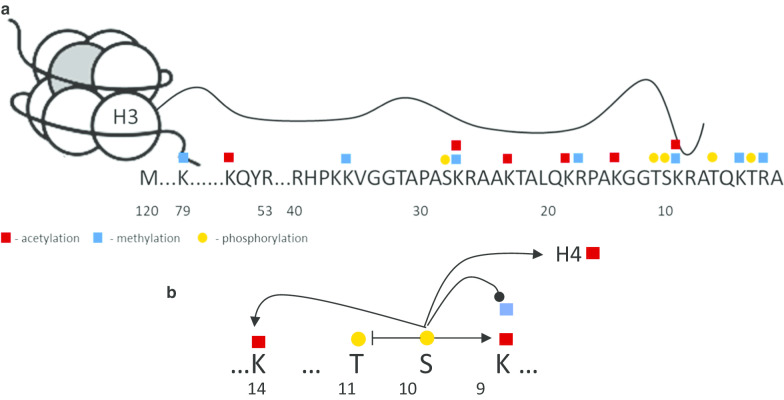
Fig. 1.
a Common posttranslational modification of histone H3 tail. Target residues for acetylation, methylation and phosphorylation in N-terminal histone region are shown. b Crosstalk between H3S10 phosphorylation and other histone post-translational modifications. In cis H3S10ph: (1) modifies binding of histone writers and inhibits phosphorylation of neighboring T11 [76]; (2) modulates epigenetic information coming from K9 methylation by regulating K9 methyltransferases [10, 56, 67–69] and demethylases [74, 75]; (3) as K9 can be both methylated and acetylated, H3S10ph also affects K9ac, it acts in synergy with this histone mark and increases efficiency of acetylation reactions [57, 105]; (4) same effects as for K9ac can be seen for K14ac [7]. H3S10ph can also affect histone post-translational modifications in trans, like histone H4 acetylation, attracting H4 acetyltransferases and protecting from deacetylase action [62, 65]