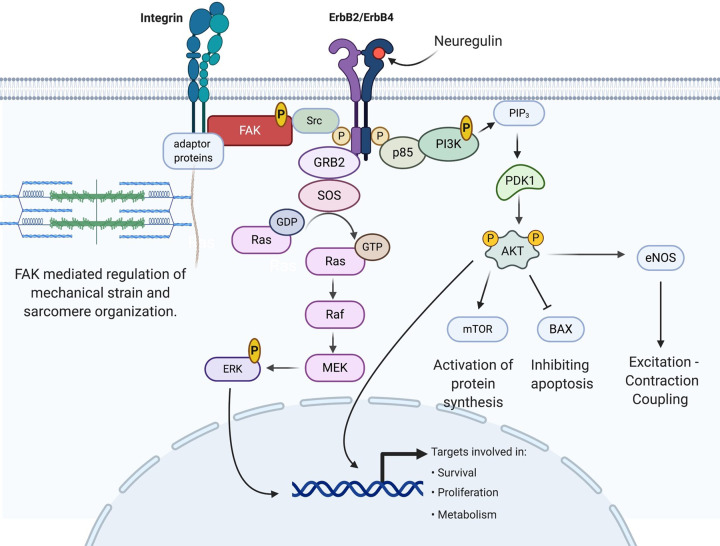
Figure 1. The NRG-1/ErbB signaling pathway in cardiac myocyte.
NRG-1 binds ErbB4 and induces dimerization with ErbB2, allowing receptor tyrosine kinase transphosphorylation. Activated ErbB receptors interact with and activate several pathways including RAS/ERK, PI3K/Akt, and Src/FAK [171–174]. Abbreviations: AKT, serine/threonine-specific protein kinase B; BAX, bcl-2-associated x protein; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; GDP, guanosine diphosphate; GTP, guanosine triphosphate; GRB2, growth factor receptor-bound protein 2; MEK, mitogen-activated ERK kinase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; PDK1, phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1; PIP3, phosphotidyl inositol (4,5,6)-triphosphate; PI3K, phosphatidyl inositol-3 kinase; p85, regulatory subunit of PI3K; Raf, proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase; Ras, Ras proteins, members of a large superfamily of small GTPases; SOS, son of sevenless; Src, proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase.