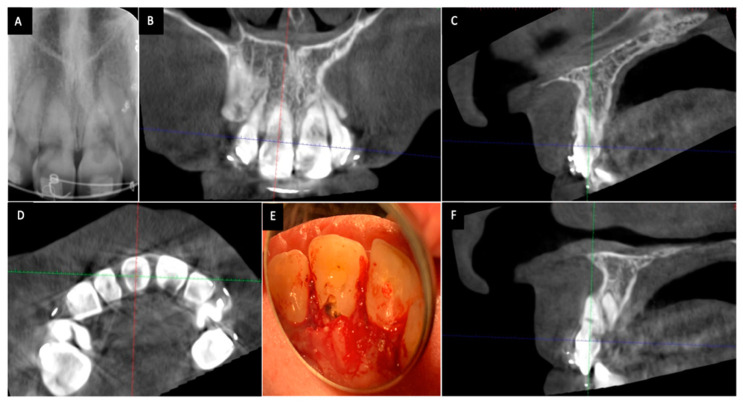
Figure 1.
Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) shows a more accurate assessment of invasive cervical resorption (ICR) lesions than two-dimensional radiographs. The size and locations of ICR lesions can be determined with CBCT. (A) Periapical radiograph showing ICR lesions in maxillary right and left incisors; (B) The coronal view of CBCT scan image showing ICR lesions in maxillary right and left incisors;(C) The sagittal view of CBCT scan image (maxillary right incisor); (D) The axial view of CBCT scan image showing the ICR lesion in maxillary right and left incisors; (E) Clinical view of ICR lesions located on the palatal surface of the teeth; (F) The sagittal view of CBCT scan image showing the ICR lesion in maxillary left incisor.