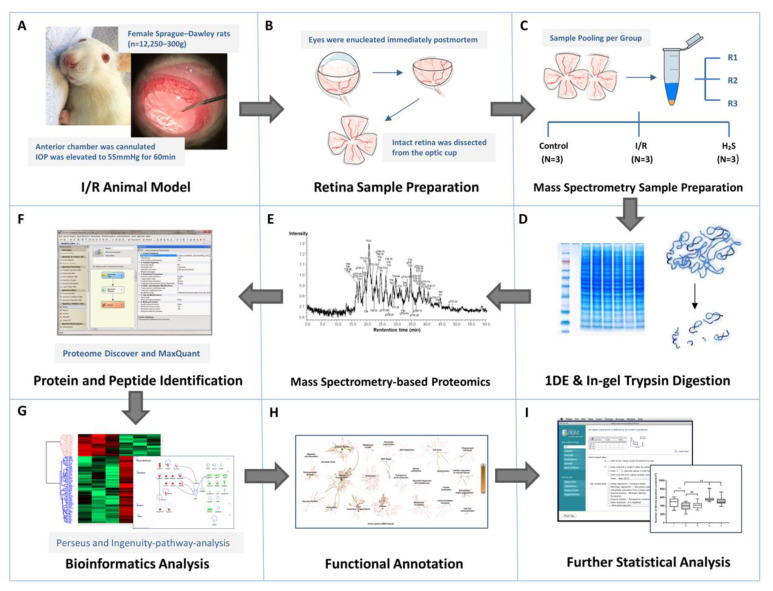
Figure 8.
Workflow overview. (A) I/R injury was induced in the left eyes of adult female Sprague-Dawley rats (n = 12), six of which received intravitreal injection of GYY4137, an H2S slow-releasing precursor, shortly before intervention. (B) Animals were executed 24 h after intervention, retinae were harvested immediately postmortem. (C–E) Retinae from contralateral eyes were designated as controls. Retinal samples were immediately weighed and lysed by T-PER tissue protein extraction reagent and Bullet Blender Storm. Six retinal protein samples from respective groups were pooled equally into three biological replicates after protein measurements, represented by RI, R2 and R3 (N = 3 replicates per group), and subsequently subjected to PAGE. The protein bands were sliced and digested by trypsin prior to proteomic analysis by LC-ESI-MS/MS. (F–H) The emerging datasets were subjected to robust bioinformatics analyses and functional annotations to identify the differential protein expressions and protein interaction networks. (I) To confirm the result of I/R injury and protective effect of H2S in retina, one quarter of each retinal sample (n = 6 per group) were subjected to immunohistochemistry staining against Brn3a for RGC quantification. The averaged RGC density was calculated per mm2. Significance of difference between groups was determined by 1-way ANOVA.