Table 1.
Overview of hydrogels with different polymer types for cartilage tissue engineering: chemical structure and features for cartilage engineering.
| Name (Abbreviation) | Chemical structure | Features for cartilage engineering | Limitations | Refs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synthetic polymers | Polyethylene glycol (PEG) | 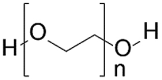 |
|
Biologically inert | [[47], [48], [49], [50], [51]] |
| |||||
| Poly (N-vinylcaprolactam) (PVCL) |  |
|
Moderate wettability, weak mechanical properties, low anti-biofouling | [42,157] | |
| |||||
| Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) | 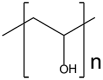 |
|
Biologically inert | [19,37,38,158] | |
| |||||
| Poly (2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) (PMPC) | 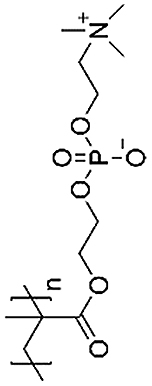 |
|
Do not support cell attachment | [[39], [40], [41],159] | |
| |||||
| |||||
| Polysaccharides | Chondroitin sulfate (CS) | 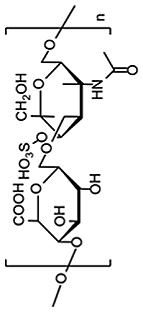 |
|
Rapid degradation | [11,34,[54], [55], [56]] |
| |||||
| |||||
| Hyaluronic Acid (HA) | 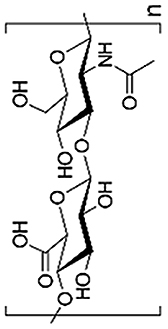 |
|
Do not support cell attachment | [62,64,68,160,161] | |
| |||||
| |||||
| Chitosan | 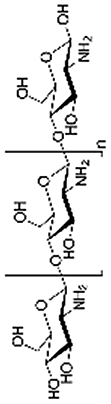 |
|
Low solubility and high viscosity | [[81], [82], [83],162] | |
| Alginate | 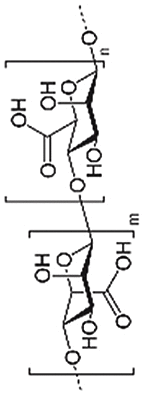 |
|
Non-biodegradable and elicit immunological responses | [[86], [87], [88], [89],91] | |
| |||||
| |||||
| Cellulose | 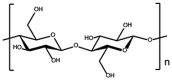 |
|
Lack of mechanical properties | [92,93,95] | |
| |||||
| Proteins | Collagen | 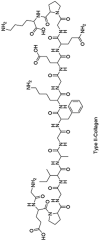 |
|
Limited number of functional groups for crosslinking | [30,99,100,103,163] |
| |||||
| Gelatin | 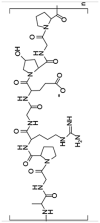 |
|
Poor mechanical properties and low thermal stability | [35,104,107,130] | |
| |||||
| |||||
| Silk Fibroin (SF) | 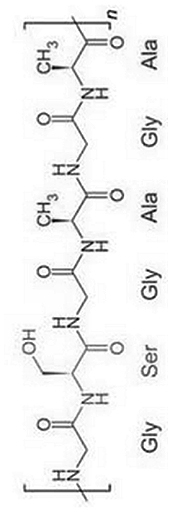 |
|
Limited options for anchoring growth factor | [111,113,114,164] | |
| |||||
| |||||
| |||||
| Sericin | 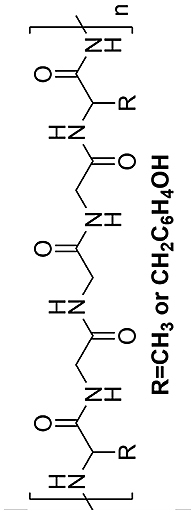 |
|
Low stability in aqueous solution | [117,165] | |
| |||||
| Fibrin | – |
|
Not chondro-permissive | [118,119] | |
| Peptides | – | – |
|
Need proper peptide design, synthesis, and purification | [125,128] |
