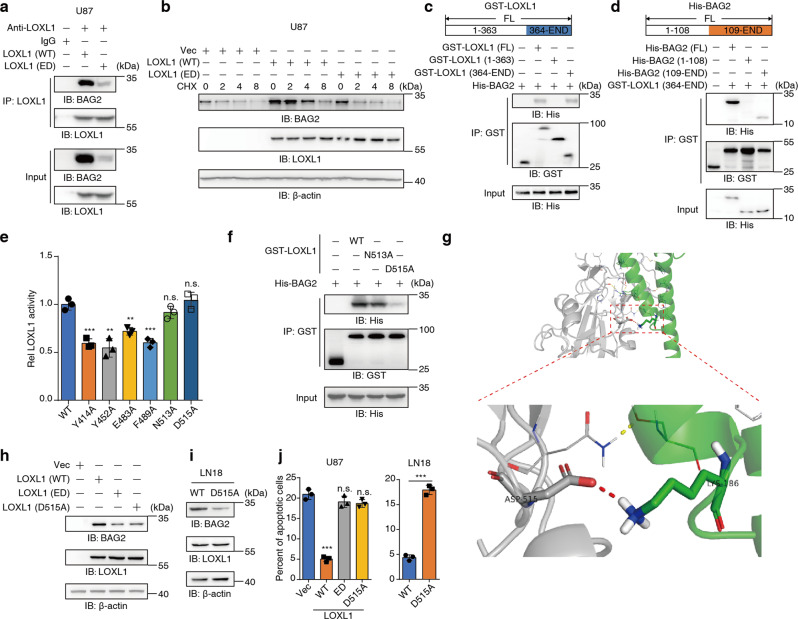
Fig. 4. LOXL1 regulates BAG2 stability through both its enzymatic activity and direct interaction with BAG2.
a, b BAG2 protein levels were increased by LOXL1. U87 cells were transiently transfected with plasmids overexpressing wild type (WT) or ED mutant LOXL1, and Vec was used as a negative control. CHX (cycloheximide, 1 μM) was used to treat cells over time (b). c GST-LOXL1, including full length (FL), 1 to 363 AAs (1-363) and 364 to the end AAs (364-END), was incubated with His-BAG2. d His-BAG2, including full length (FL), 1 to 108 AAs (1-108) and 109 to the end AAs (109-END), was incubated with GST-LOXL1. e Molecular simulations were performed to find the potential sites required for interacting with the BAG domain of BAG2. Then, measurement of LOXL1 enzymatic activity was performed. f D515A mutation reduced the direct interaction between LOXL1 and BAG2. GST-LOXL1 (including WT, N513A and D515A) was incubated with His-BAG2. g The interaction diagram of LOXL1-D515 with BAG2-K186. h U87 cells were transiently transfected with plasmids overexpressing WT, ED or D515A mutant LOXL1. i Endogenous BAG2 was determined with a specific antibody when LOXL1 D515 was mutated into A515. j The reduced interaction between LOXL1 and BAG2 decreased the ability of glioma cells to resist apoptosis.