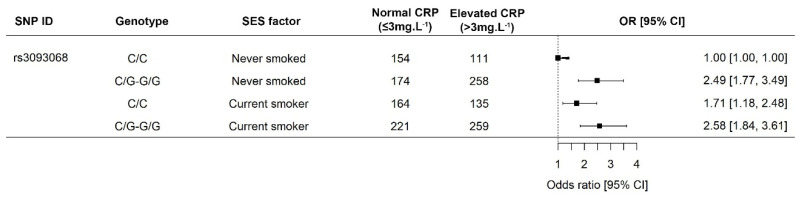
Figure 1.
Interaction between tobacco smoke and rs3093068 in the Prospective Urban and Rural Epidemiology study—North West arm. The minor allele is associated with increased CRP concentrations, which are further increased in smokers. Men were more likely to be current smokers (59.5% vs. 47.6%; p < 0.0001). Homozygous smokers for the minor allele had a 71% increased risk of presenting with elevated CRP concentrations. Abbreviations: CRP, C-reactive protein; C, cytosine; CI, 95% confidence interval; G, guanine.