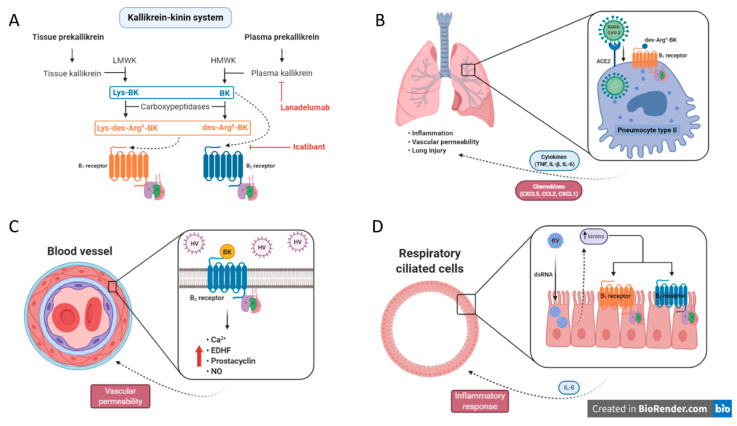
Figure 2.
The role of kinin system in viral infections. (A) The kallikrein–kinin pathways and their intermediates, including enzymes, active metabolites, and receptors. In addition, the current pharmacological targets to modulate the system (e.g., lanadelumab and icatibant). Dashed lines designate the ligands and their respective receptors. (B) Hypothetical mechanism of crosstalk between SARS-CoV-2 and the kinin system, in which it could be one of the responsible routes for the worsening of Covid-19 clinical evolution. (C) Hantavirus (HV) modulates the bradykinin (BK)–B2 receptor axis promoting the release of Ca2+, endothelium-derived hyperpolarization factor (EDHF), prostacyclin and, nitric oxide (NO). Consequently, increasing the vascular permeability. (D) The “common cold virus”, called Rhinovirus (RV), has been suggested to enhance the expression of BK receptors (B1 and B2) by increasing the kinin agonists (i.e., BK, kallidin, and des-Arg9-BK) in nasal secretion of patients with respiratory syndromes. LMWK = low molecular weight kininogen; HMWK = high molecular weight kininogen; ACE2 = angiotensin-converting enzyme 2.