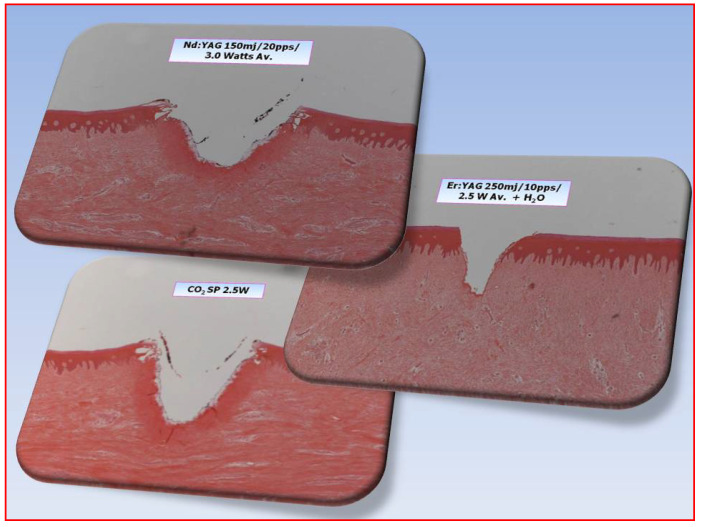
Figure 6.
Comparative light micrographs of laser interaction with porcine oral soft tissue. Top: Nd:YAG 1064 nm (an example of the shorter wavelengths employed), causes a wider, crater-shaped area of ablation, with some areas of thermal conduction. Right: Longer wavelengths such as FRP Er:YAG 2940 nm create a sharper “V” shaped incision, whereas Bottom: CO2 10,600 nm, being a gated CW emission, results in some features of the other two—surface configuration ascribable to absorption in water, but some thermal spread arising from a comparative lack of thermal relaxation.