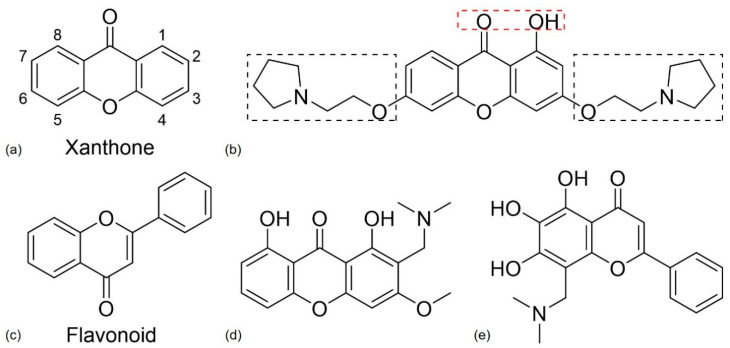
Figure 11.
(a,c) Chemical structure of xanthone and flavonoid nucleus, respectively. (b) Chemical structure of the most promising xanthone derivative according to Kou et al. [111]. The substituents in the red rectangle can work as a metal chelating agent and and antioxidant, while the substituents in the black rectangle lead to antioxidant and anti-acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity. Adapted from [111]. (d,e) Chemical structures of the most promising xanthone and flavone derivatives, respectively, obtained by Cruz et al. [101] for AD.