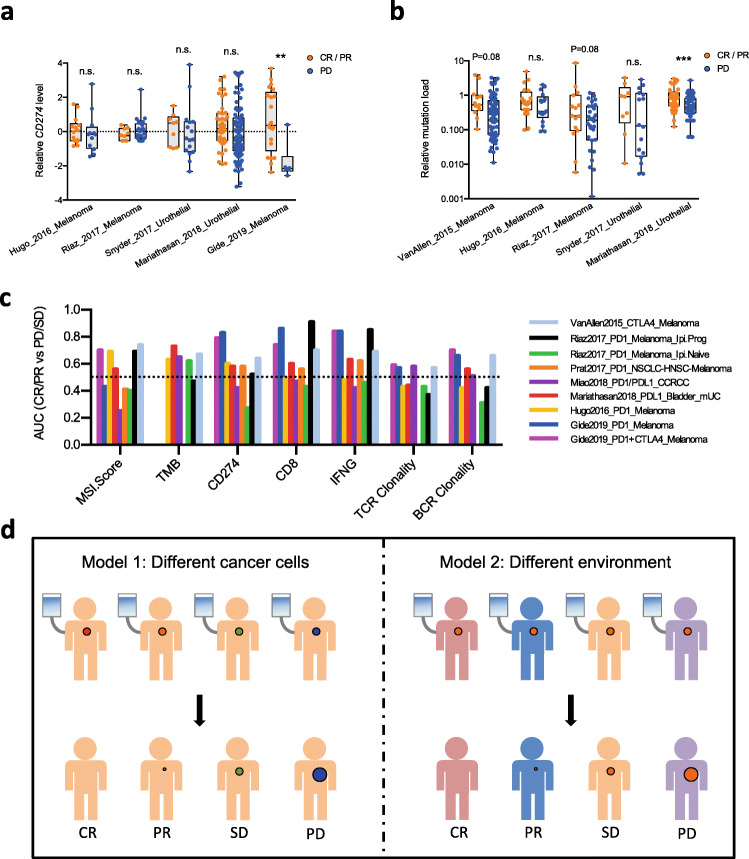
Fig. 1.
Performance of biomarkers is incoherent across different ICB clinical cohorts. a CD274 level significantly correlates with ICB response in Gide et al., but not the other studies. b Tumor mutation burden significantly correlates with ICB response in the Mariathasan et al. study, but not in the Hugo et al. or Snyder et al. studies (boxplot shows the minimum, first quartile, median, third quartile, and maximum values of each group; n.s., not significant; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; Student’s t test with Benjamini-Hochberg adjustment of P values for multiple comparison). c Systematic evaluation of multiple biomarkers of ICB response in different clinical cohorts reveals inconsistent performance. d Two non-mutually exclusive models can explain the inconsistent performance of biomarkers in different clinical cohorts. Model 1 assumes that different mutation profiles and epigenetic status of cancer cells from different tumors (colored dots) determine the heterogeneous response (size of dots) after ICB treatment (syringe). Model 2 assumes that host-specific factors determine response