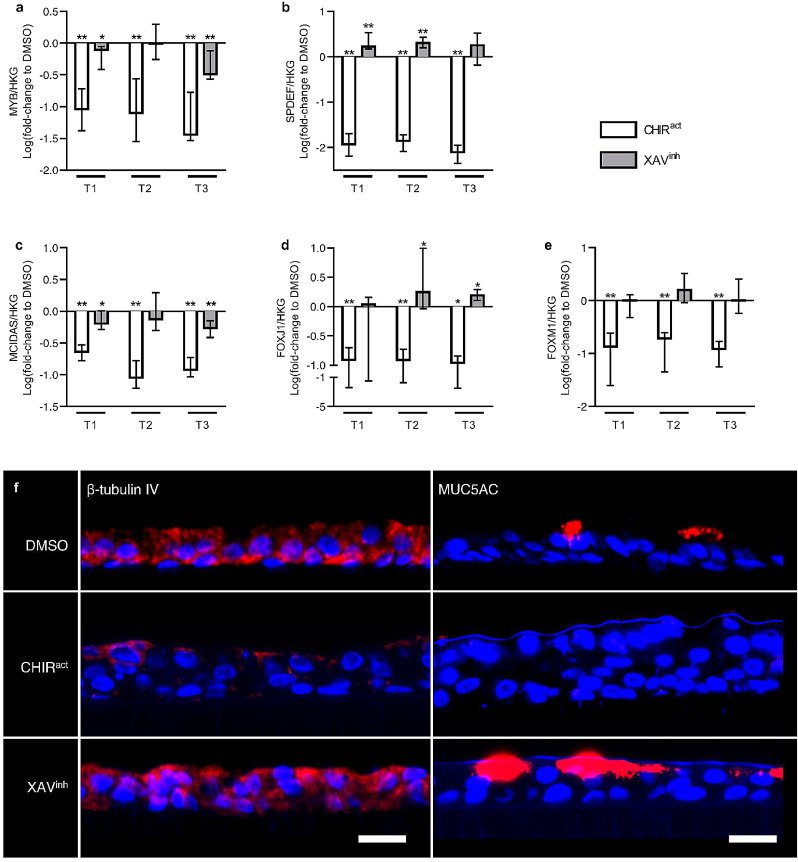
Fig. 5.
WNT modulation regulates AE cells differentiation.
a) CHIR99021-induced WNT activation strongly downregulated the expression of MYB, an early epithelial differentiation marker, at all time periods. XAV939-induced WNT inhibition also downregulated it at T1 and T3, although in a lesser extent.
b) WNT activation inhibited the commitment towards goblet cells, as SPDEF expression was completely suppressed by CHIR99021. Conversely, WNT inhibition increased SPDEF expression.
c-d) WNT activation repressed the specification and commitment towards ciliated cells, as CHIR99021 decreased the expression of MCIDAS (c) and FOXJ1 (d). WNT inhibition decreased MCIDAS (c) expression but increased FOXJ1 (d), demonstrating an opposite effect on specification or commitment towards ciliated cells.
e) WNT activation by CHIR99021 decreased the expression of FOXM1, a transcription factor involved in the commitment towards club cells, while WNT inhibition by XAV939 had no significant effect.
f) Representative pictures of ALI-reconstituted epithelia, cultured under vehicle condition (DMSO), WNT activation (CHIR99021) or WNT inhibition regimen (XAV939). The epithelium were stained for ciliated cells (β-tubulin IV, left panel) and goblet cells (MUC5AC, right panel), showing a sharp decrease of both cell types upon WNT activation. Conversely, WNT inhibition increased MUC5AC expression and tended to increase β-tubulin IV expression.
*, ** indicate p-values of less than 0•05 and 0•01, respectively (analysed using the Mann-Whitney test). Columns and bars in the graphs represent medians ± interquartile range. Scale bars, 20 µm. CHIRact, CHIR99021-induced WNT activation condition; HKG, housekeeping genes; XAVinh, XAV939-induced inhibition condition.