Fig. 4. Molecular interactions underlying CST decameric supercomplex formation and testing the dimer stapling model.
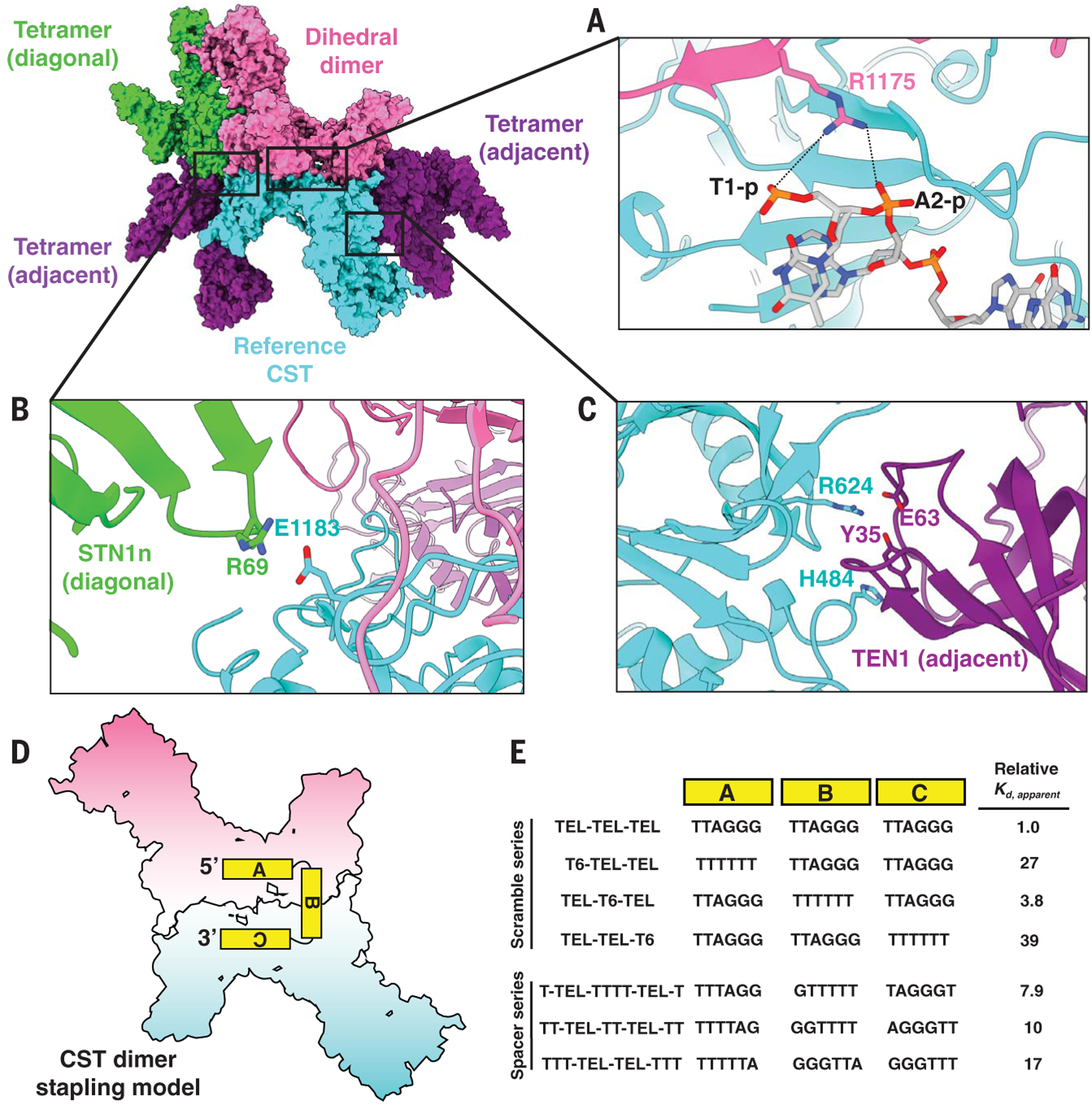
(A to C) The reference CST (cyan) is flanked by four CST complexes—a dihedral dimer (opposite, pink) and three tetrameric partners (one diagonal neighbor, green, and two adjacent neighbors, purple). (A) CTC1 R1175 from the dihedral dimer neighbor (pink) is pointing toward ssDNA bound to the reference CTC1 (cyan), with the black dashed lines representing feasible ionic interactions between R1175 and phosphodiester groups of the ssDNA. (B and C) Identified intermolecular interactions between CTC1, STN1, and TEN1 at interfaces of the decameric supercomplex. (D) CST dimer stapling model with an 18-nt ssDNA molecule. The two monomers are separately colored as pink and cyan for visual clarity. (E) Changes in CST DNA-binding affinity (Kd,apparent) relative to that of 3xTEL with oligo-T substitution of block A, B, or C of 3xTEL (Scramble series). The molecular distance between the TTAGGG sequences of blocks A and C was also varied, and the impact on CST relative DNA-binding affinity was measured (Spacer series). TEL-TEL-TEL oligo is also known as 3xTEL. The relative DNA-binding affinity values are reported to two significant figures; measured values and error analysis are in table S1.
