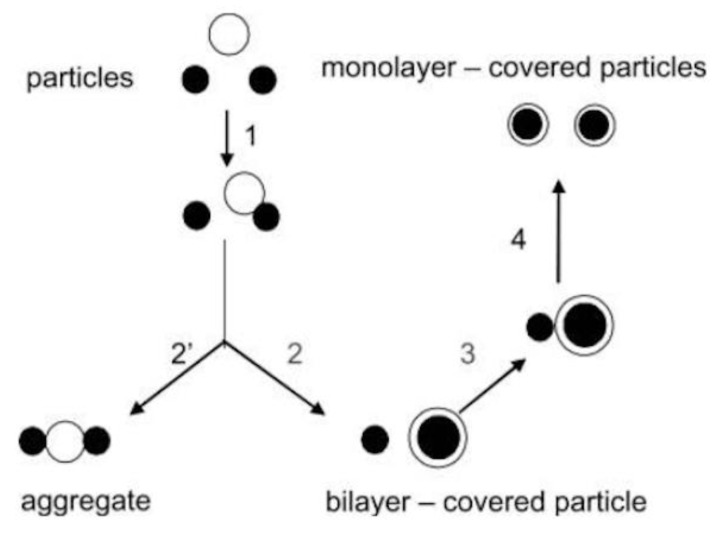
Figure 17.
The interaction between one bilayer vesicle and two particles. In the first step (step 1), electrostatic and/or van der Waals and/or hydrophobic attraction leads to aggregation of a vesicle and a particle. These same interaction forces may disrupt the vesicle bilayer and promote bilayer adsorption onto the microsphere (step 2) and/or further aggregation with the other microsphere (step 2′). The adsorbed bilayer may attract the second microsphere (step 3). The hydrophobic interaction between an eventually hydrophobic surface and the hydrocarbon chains in the bilayer may completely destroy the bilayer structure, flip-flopping the hydrocarbon chains onto the particle surface and generating a monolayer coverage on each microsphere (step 4). Adapted from [206] with permission from Elsevier, Copyright 1999.