Figure 3. De novo CENP‐A deposition is impaired in the absence of CENP‐B.
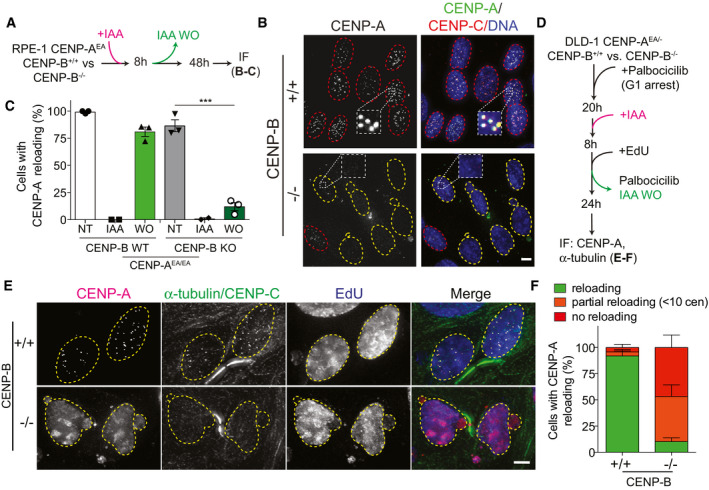
- Schematic illustration of the CENP‐AOFF/ON cycle performed in the experiments shown in B, C.
- Representative images of de novo CENP‐A reloading in CENP‐B wild‐type (+/+) and CENP‐B knock‐out (−/−) cells. Cells with centromeric CENP‐A are marked with a red dashed contour line, while a yellow contour lines mark cell without centromeric CENP‐A. Scale bar, 5 μm.
- Quantification of relative number of RPE‐1 cells with centromeric CENP‐A in the indicated conditions. Each dot represents one experiment with at least 20 cells per condition. Error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM) from 3 independent experiments. Unpaired t‐test, ***P = 0.0003.
- Schematic representation of experiments shown in E, F.
- Representative images of DLD‐1 CENP‐B (+/+) or (−/−) cells in late M phase following one CENP‐AOFF/ON cycle. EdU staining was used to confirm successful wash‐out of palbociclib and cell progressing through S‐phase. Yellow dashed lines contour nucleus of cells in late M phase. Scale bar 5 μm.
- Quantification of indicated events observed in late M phase cells in the indicated cell lines. Error bars show SEM from 4 independent experiments.
