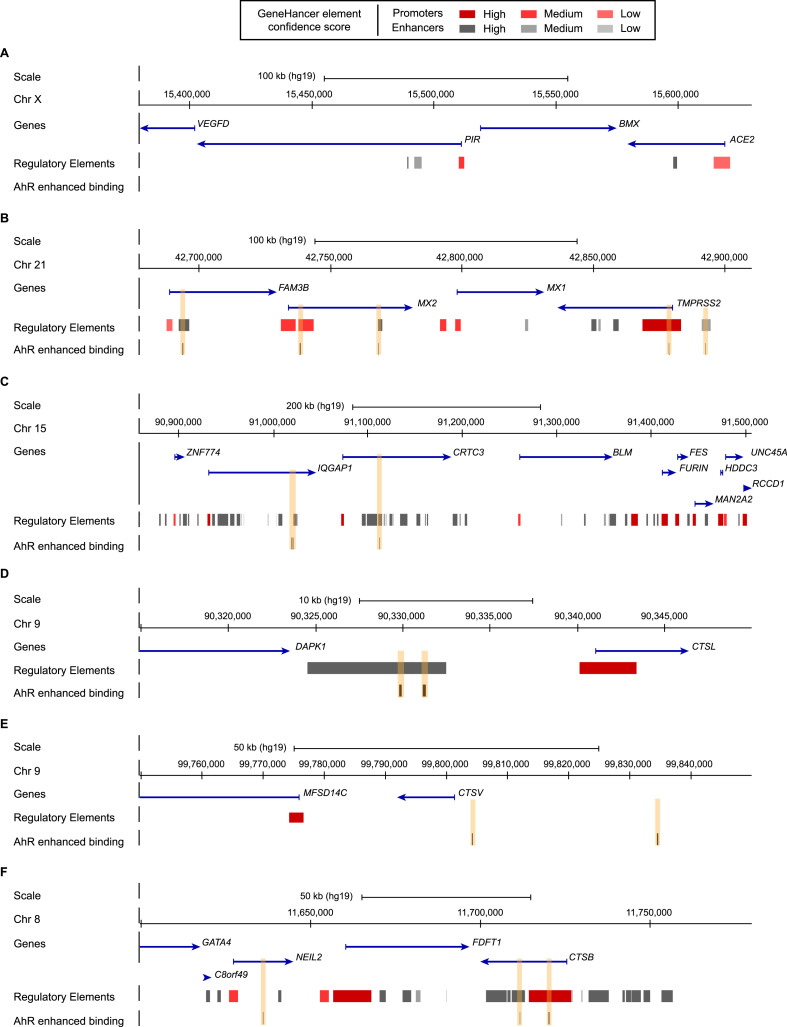
Fig. 4.
AhR binding in ACE2, TMPRSS2, FURIN, CTSL, CTSV and CTSB regions upon TCDD exposure. Schematic representation from the UCSC Genome browser (reference human genome GRC37/hg19) highlighting the regions of (A) ACE2 (chrX:15,380,000–15,630,000), (B) TMPRSS2 (chr21:42,678,000–42,910,000), (C) FURIN (chr15:90,860,000–91,507,000), (D) CTSL (chr9:90,315,000–90,350,000), (E) CTSV (chr9:99,750,000–99,850,000) and (F) CTSB (chr8:11,600,000–11,780,000). The panels show from the top to bottom: the genomic coordinates on chromosome, the position of the genes and their orientations retrieved from the NCBI RefSeq Select database (one representative transcript per protein-coding gene), the position of the regulatory elements with enhancers represented in grey and promoters represented in red from GeneHancer Double Elite database, the position of the AhR binding sites enhanced upon TCDD exposure highlighted by orange boxes. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)