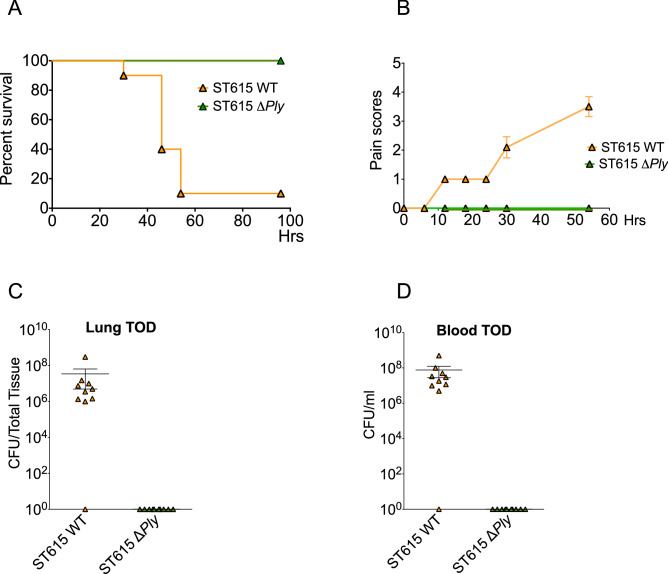
Figure 5.
Pneumolysin is indispensable to the invasive properties of pneumococcal ST615. (A) Upon challenge with ST615 wild-type (WT) or ST615Δply pneumococci, mice were monitored for the development of visual signs of disease (n = 10 mice per group; mean ± SEM). Pain scores were assigned as follows 1: hunched, 2: starry/piloerecti, 3: lethargic, 4: moribund, 5: dead. (B) Kaplan–Meier survival chart monitoring the number of mice succumbing to disease over 3 days upon challenge with ST615 WT versus ST615Δply. (C,D) Pneumococcal viable counts in lung tissues (C, CFU/tissue) or and peripheral blood (D, CFU/ml) upon intranasal infection with ST615ΔPly compared with ST615 WT pneumococci at time of death (TOD). Data are represented as mean ± SEM (n = 10 mice per group). Each mouse is represented by a symbol.