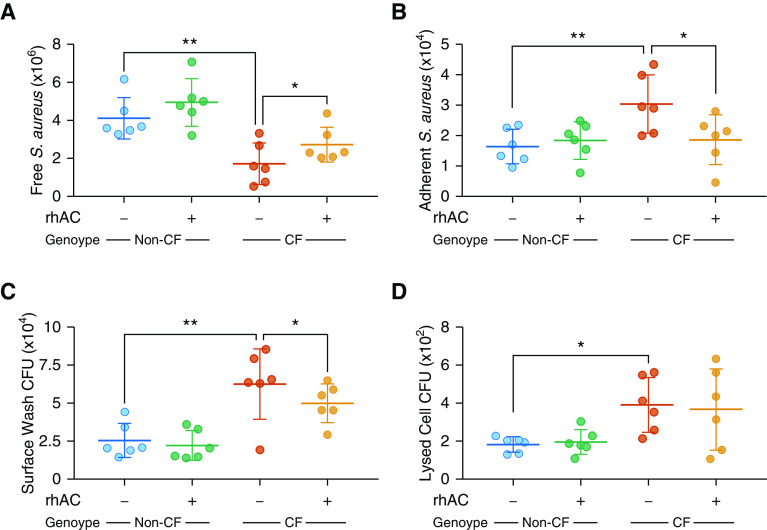
Figure 8.
Effect of rhAC (recombinant human acid ceramidase) treatment on infection in cystic fibrosis (CF) airway epithelial cell cultures. (A and B) Number of fluorescently labeled heat-killed Staphylococcus aureus retrieved from apical surface washes (A) and adherent to apical surface (B) in CF and non-CF fully differentiated cultures with and without prior rhAC treatment. For representative images, see Figure E6 in the online supplement. (C and D) Colony-forming unit counts of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from apical surface washes (C) and whole-cell lysates (D) (after washing, suggesting internalization) from CF and non-CF cultures with and without prior rhAC treatment. Live P. aeruginosa were added to the apical surface of cultures and allowed to proliferate for 24 hours. Throughout, n = 6 separate experiments. Individual data points are presented along with the mean (horizontal line) ± SD (error bars). For statistical tests used, see the online supplement. *P < 0.05 and **P ≤ 0.01.