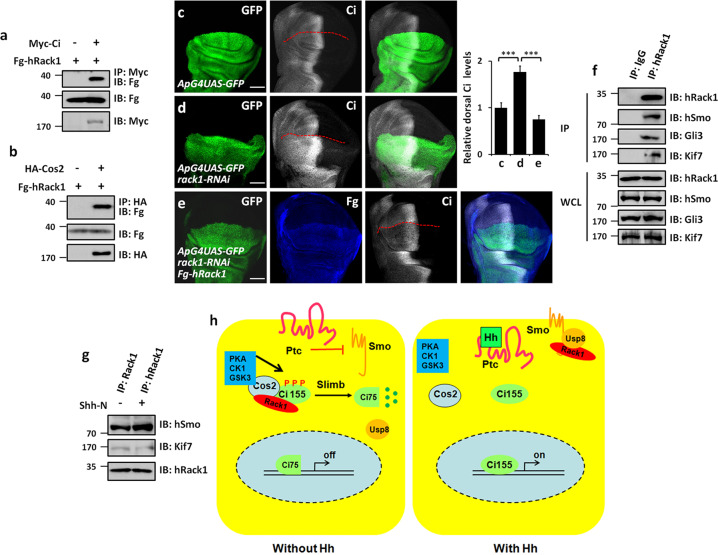
Fig. 7. The regulation of Rack1 on Hh pathway is conserved in mammalian cells.
a hRack1 interacted with Ci in S2 cells. b hRack1 bound Cos2 in S2 cells. c–e Wing discs of control (c), rack1 RNAi (d), and simultaneously expressing Fg-tagged hRack1 and rack1 RNAi (e) was stained to show GFP (green), Fg (blue), and Ci (white). Quantification analyses were shown on right (n = 5). Of note, overexpression of hRack1 could rescue Ci upregulation induced by rack1 knockdown. f IBs of immunoprecipitates (top four panels) or lysates (bottom four panels) from HEK 293T cells. Notably, hRack1 could pull-down hSmo, Gli3, and Kif7. g Shh-N stimulation strengthened hRack1–hSmo interaction, while diminished hRack1–Kif7 association. h A proposed model of Rack1 regulating Hh pathway. In the absence of Hh, Rack1 forms a complex with Ci and Cos2, leading to Slimb-mediated Ci degradation (left). In the presence of Hh, Rack1 dissociates from Ci–Rack1–Cos2 complex and recruits Usp8 to Smo, resulting in Smo deubiquitination and cell surface accumulation (right). Scale bars: 50 μm for the wing disc (c–e).