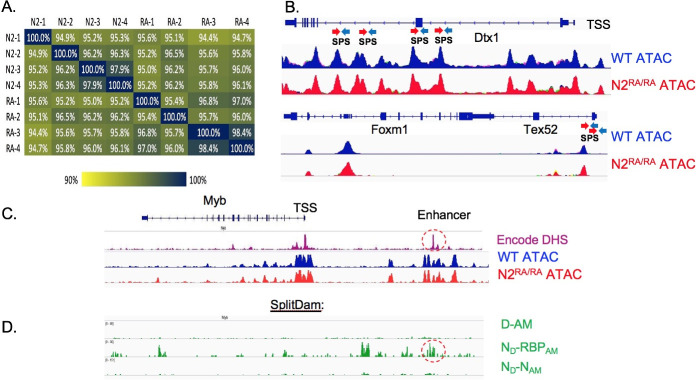
Fig 7. Mite-infested N2RA/RA activate a proliferation module in MZB.
A. Spearman correlation table measures ATAC-Seq peaks similarity matrix between 8 mice (4 in each genotype). All are >92% similar. B-C. ATAC-Seq data reveal that DNA accessibility was not altered near the Notch target Dtx1 that is down-regulated in expression in N2RA/RA animals (B.). WT in blue, N2RA/RA in red. Location of validated enhancers containing SPSs are shown. Note, each dimer-dependent site can be composed of either 2 canonical sites (red arrows) or 1 canonical and 1 noncanonical site (blue arrow). Close inspection of ATAC peaks and the proliferation drivers FoxM1i (B.) or Myb (C.) loci. D. The Myb locus was analyzed for chromatin accessibility (Encode DHS and ATAC-seq data generated in this study) and DNA methylation by DAM methyl transferase complementation (SplitDAM). The methylation patterns generated by control D/AM halves are compared to methylation patterns generated by Notch-D/RBPj-AM pairs (which recognizes both dimer-dependent and dimer-independent sites) and Notch-D/Notch-AM pairs (which recognizes only dimer-dependent sites). See text and [45] for additional details. ATAC-Seq, Assay for Transposase Accessible Chromatin sequencing; D/AM, complementing halves of DAM; DAM, DNA adenine methyltransferase; DHS, DNAse hyper sensitive; MZB, marginal zone B-cell; N2RA/RA, Notch-D, Notch1 fused to the D half of DAM; Notch2 Arg N2R1934to Ala substitution, homozygous; RBPj-AM, recombinant binding protein for immunoglobulin Kappa j region fused to AM half of DAM; SPS, sequence-paired site; TSS, transcription start site; WT, wild-type.