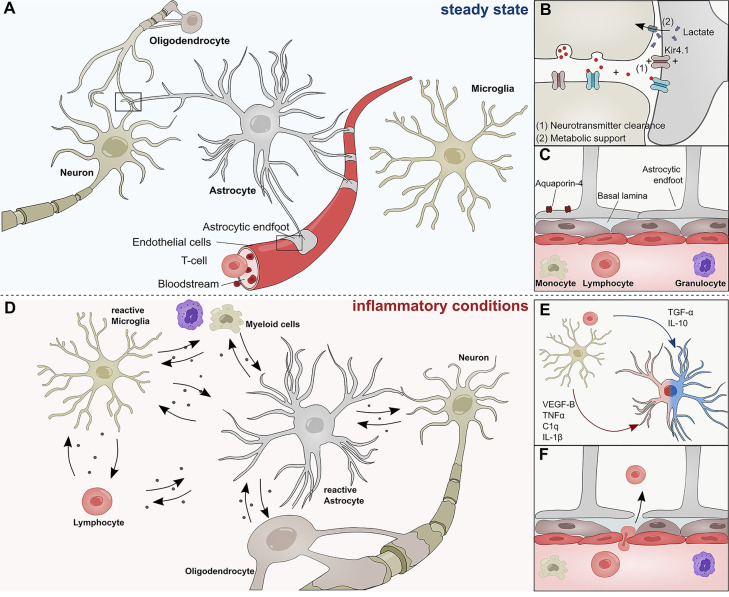
Figure 1.
Role of astrocytes in the steady state and inflammatory conditions. (A) Astrocytes interact with neurons, oligodendrocytes, microglia, and cells of the BBB during steady state conditions. (B) Astrocytes form tripartite synapses with neurons and regulate their synaptic transmission through metabolic support and the clearance of neurotransmitters. (C) Astrocytic endfeet line the cerebral vasculature and are a constituent of the blood brain barrier, thus limiting the infiltration of pathogens and peripheral immune cells into the central nervous system. Their endfeet express high levels of Aqp-4 and form a close interaction with pericytes and the basal lamina of the brain parenchyma. (D) During inflammatory conditions, reactive astrocyte secrete a plethora of inflammatory mediators that regulate functions of myeloid cells, lymphocytes, oligodendrocytes, neurons, and microglia. (E) Soluble inflammatory mediators derived from mircoglia and other immune cells differentially induce pathogenic (red) or protective (blue) astrocyte functions. (F) Peripheral immune cells pervade the BBB during inflammatory conditions and transgress into the CNS. C1q, Complement component 1q; IL-1β, Interleukin-1 β; IL-10, Interleukin 10; TNF-α, Tumor necrosis factor α; TGF-α, Transforming growth factor α; VEGF-B, Vascular endothelial growth factor B.