Figure 3.
UBE3A Is Imprinted and Aberrantly Localized in Angelman Syndrome hCOs
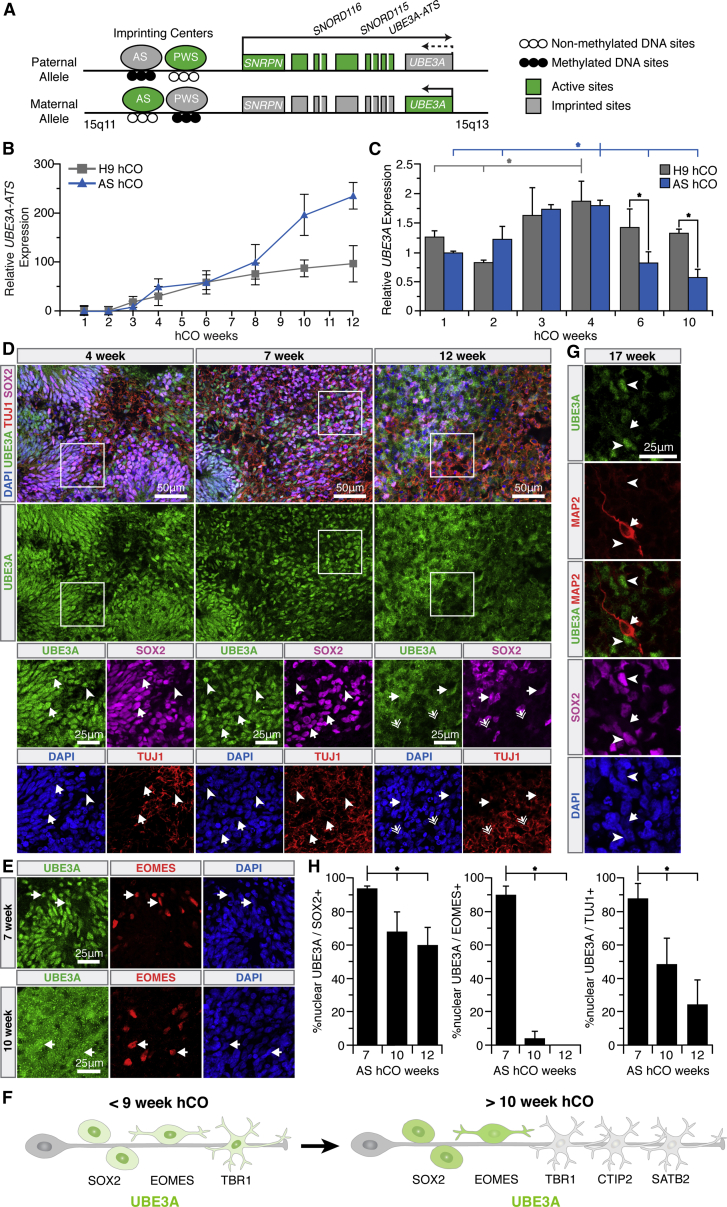
(A) The UBE3A locus.
(B and C) qRT-PCR measurements of mRNA levels of UBE3A-ATS (B) and UBE3A (C) in neurotypical and AS hCOs, normalized to HPRT, ratioed to 1 week AS hCOs. Error bars are 95% confidence intervals. (B) p < 0.05 t test against null-slope hypothesis. n = 3 independent experiments with three to five organoids in each. (C) ∗p < 0.05, full tick marks compared with half tick marks by one-way ANOVA with Tukey-Kramer post hoc. n = 3 independent experiments with three to five organoids in each.
(D, E, and G) UBE3A expression and localization in AS hCOs. (D) Salient nuclear UBE3A in SOX2+ progenitors of 4–12 week AS hCOs (arrows). Salient nuclear UBE3A in 4–7 week TUJ1+/SOX2−neurons (arrowheads) is lost in 12 week AS hCOs (double arrows).
(E) Strong nuclear UBE3A in 7 week EOMES+ cells (arrows) is weakened at 10 weeks in AS hCOs.
(F) Summary of dynamic UBE3A localization in AS hCOs.
(G) UBE3A is absent in 17 week MAP2+/SOX2− neurons (arrows). SOX2+ progenitors still express some paternal UBE3A (arrowheads).
(H) Percentage of nuclear UBE3A in 7–12 week AS hCOs. ∗p < 0.05, full tick marks compared with half tick marks by one-way ANOVA with Tukey-Kramer post hoc analysis, n = 3 independent experiments with two organoids in each. Error bars are 95% confidence intervals.
(See also Figure S4.)