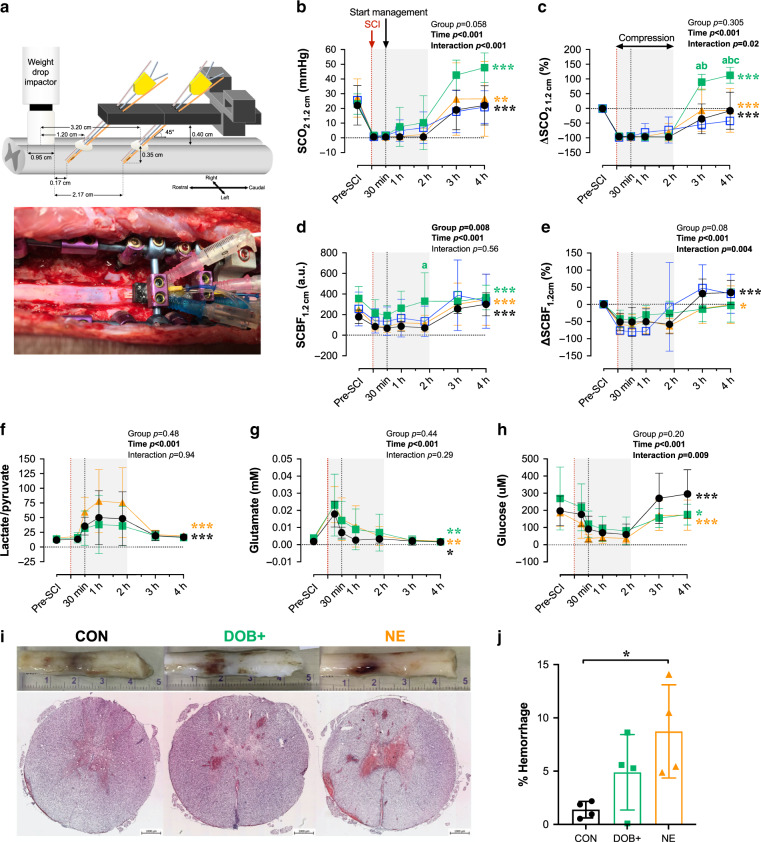
Fig. 4. Impacts of dobutamine (DOB) and norepinephrine (NE) on the spinal cord acutely post-SCI.
a Setup for intraparenchymal monitoring. A fixation device is secured to the spinal column and probes are inserted through the dura 1.2 cm and 3.2 cm caudal to the center of the impactor. All data are shown for 1.2 cm probes. Data from 3.2 cm probes are provided in Supplementary Table 6. b Data points are means and error bars represent s.d. for animals receiving no treatment (control, CON; n = 8), high-dose DOB (DOB+; n = 4), low-dose DOB (DOB−; n = 3), and NE (n = 7). Improvements to spinal cord oxygenation (SCO2) occur after decompression (i.e. 2 h post-SCI), but are most pronounced in DOB+. c When expressed as a percent change form baseline, ∆SCO2 is significantly augmented in DOB+ compared to all groups by 4 h post-SCI. d Spinal cord blood flow (SCBF) is augmented in CON, NE, and DOB+ following decompression, and DOB+ notably augmented absolute SCBF at 2 h post-SCI. e However, when expressed as percent change from baseline, SCBF was only altered in CON and NE over the treatment period. f The lactate/pyruvate ratio does not significantly increase after management onset (i.e. 30 mins post-SCI) with DOB+, but is increased in NE and CON. g In all groups, glutamate becomes progressively reduced and h glucose is increased following decompression (i.e. 2 h post-SCI). Sufficient microdialysis data were only acquired in n = 2 for DOB−, thus DOB− data were excluded from analyses. i Representative cords and histological stains show pronounced hemorrhaging with NE. Measures of hemorrhage were averaged over five separate sections per animal. j Animals receiving NE have augmented hemorrhaging at the injury epicentre, which is mitigated by DOB+. See Fig. 3 for symbol definitions and statistical details. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. ap < 0.05 vs CON; bp < 0.05 vs DOB-; cp < 0.05 vs NE. Within-group comparisons between 30 mins and 1 h to 3 h post-SCI are available in Supplementary Tables 6 and 7. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.