Figure 4.
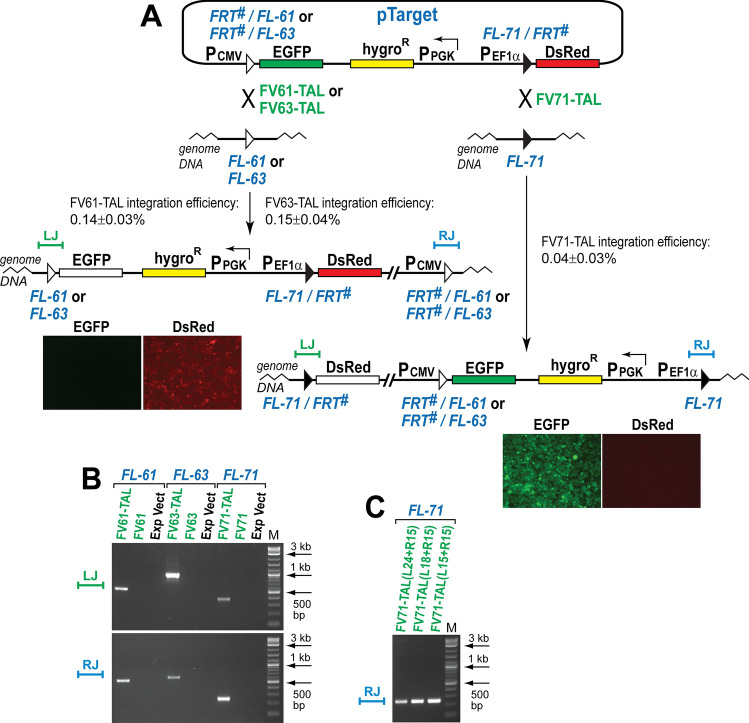
Flp-TAL variants target FRT-like sequences FL-61, FL-63, and FL-71 in their native chromosomal environment. (A) Schematics of the integration assays. The reporter pTarget can be integrated either into FL-61, FL-63, or FL-71 depending on the specificity of the Flp-TAL recombinase and the version of pTarget: FL-61/FL-71 or FL-63/FL-71. Upon integration of pTarget into FL-61 or FL-63 the resultant cells become hygromycin resistant and red, while upon integration into FL-71, the cells become hygromycin resistant and green (images of the individual expanded hygroR/red and hygroR/green colonies are shown as examples). The analysis of the individual colonies was performed in two biological replicates. LJ and RJ mark the locations of the left and right junctions of the integrated reporter and genomic DNA, respectively; diagnostic PCR at these locations was used to determine the authenticity of the reporter integration. (B) PCR analysis of the pooled hygroR colonies generated in the experiments with the Flp-TAL recombinase, the ‘plain’ recombinase variant, and the ‘empty’ expression vector. LJ, RJ, the PCR analysis of the left and right junctions of pTarget integrated into the respective genomic sequences; M, DNA ladder (NEB, 2-log). (C) PCR analysis of the pooled hygroR colonies generated in the integration experiments with three combinations of the FV71-TAL recombinases: FV71-TAL(L24) + FV71-TAL(R15), FV71-TAL(L18) + FV71-TAL(R15) and FV71-TAL(L15) + FV71-TAL(R15). The diagnostic PCR analysis was performed at the right junction.