Figure 3.
Allele Quantification in Sib Selections via dPCR and NGS
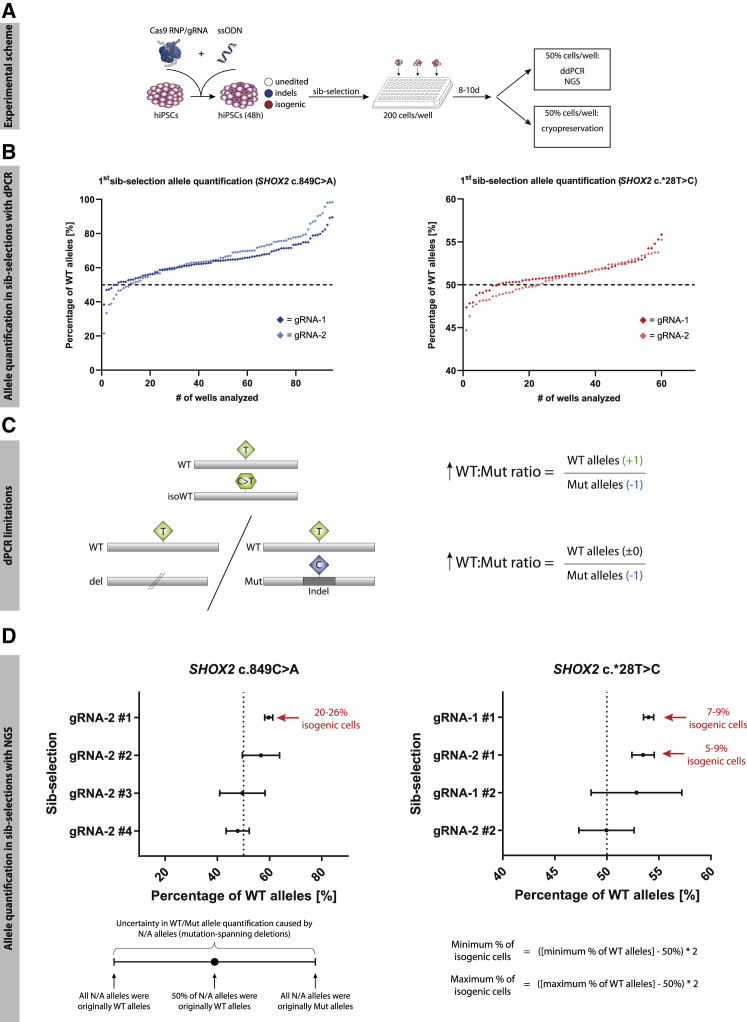
(A) Experimental scheme of gene-editing approach.
(B) WT and Mut alleles were quantified in each sib selection 10 days after transfection via dPCR. Each dot represents the result for one sib selection. The dotted line marks the 50% WT allele percentage expected in unedited hiPSCs. Sib selections with the highest abundance of WT alleles were thawed and re-analyzed.
(C) Limitations of dPCR in allele quantification: due to the PCR-based allele detection, non-amplifiable Mut alleles can lead to shifts in the WT/Mut ratio, similar to what is caused by isogenic subpopulations.
(D) Allele quantification via NGS: alleles with SHOX2 c.849- and SHOX2 c.∗28-spanning deletions cause an uncertainty in allele quantification that is addressed by defining those alleles as all WT or all Mut. The resulting span of possible allele ratios is represented as error bars. Sib selections in which an increased WT/Mut allele ratio is not solely explicable by a loss of detectable Mut alleles were chosen for single-cell cloning. The percentage of isogenic cells was calculated with the given formula. Abbreviations: Indel, insertion/deletion; N/A, non-assignable.