Figure 4.
Single-Cell Cloning with Sib Selections and Screening for Isogenic Clones
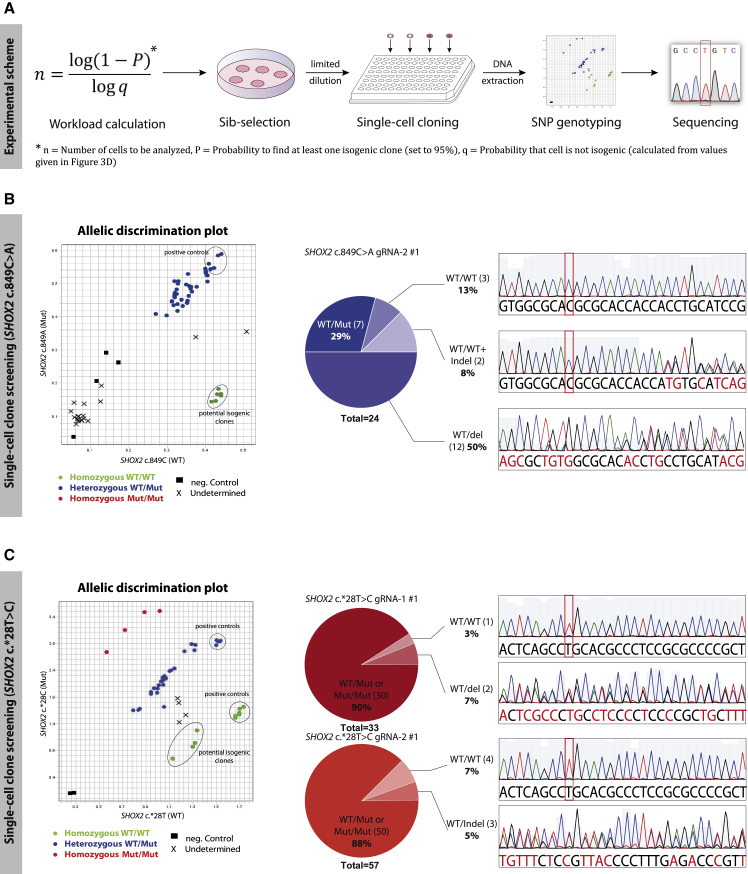
(A) Experimental scheme for single-cell cloning and screening: the number of clones needed to be analyzed was calculated with a binomial distribution function. Sib selections with isogenic subpopulations were thawed for single-cell cloning via limited dilution. Clones were screened via TaqMan probe-based SNP genotyping, and potential homozygous WT clones were confirmed with Sanger sequencing.
(B) Screening for isogenic clones derived from heterozygous SHOX2 c.849C>A cells: 24 single-cell clones were genotyped and sequenced. In 5/24 clones (21%) the mutation was corrected back to WT, with 3 clones showing no additional mutations several hundred nucleotides up- and downstream.
(C) Screening for isogenic clones derived from heterozygous SHOX2 c.∗28T>C cells: single-cell-derived clones were genotyped. Ten annotated homozygous WT clones were sequenced to confirm the loss of the SHOX2 c.∗28T>C mutation. In 5/10 clones the mutation was repaired precisely back to WT, in the other 5/10 clones, deletions on the Mut allele explained the false annotation. Abbreviations: SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism, here, SHOX2 c.849C>A and SHOX2 c.∗28T>C; Indel, insertion/deletion.
See also Figures S3 and S4, Tables S3 and S5.