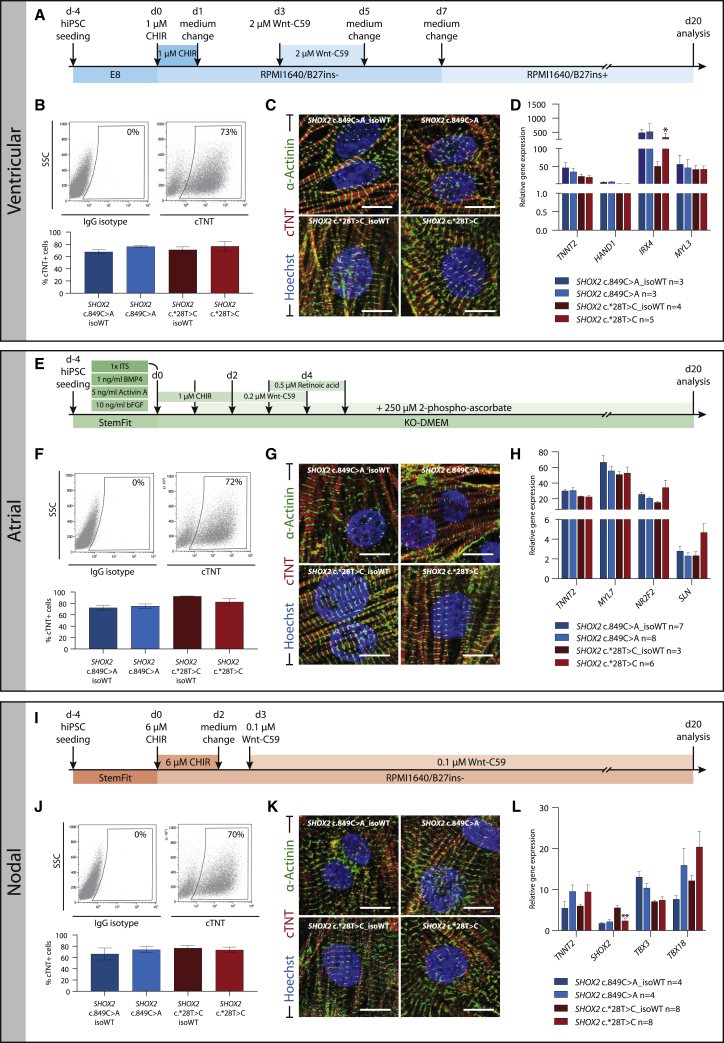
Figure 6.
Differentiation of Patient-Specific and Isogenic Control hiPSCs into Cardiomyocyte Subtypes
(A, E, and I) hiPSCs were differentiated into ventricular- (A–D), atrial- (E–H), and nodal-like (I–L) cardiomyocytes using the given differentiation schemes. (B, F, and I) Flow-cytometry analysis revealed similar numbers of cTNT+ cells in isogenic pairs, indicating an unimpaired differentiation capacity in patient lines. Top: Representative flow-cytometry dot plots for IgG isotype control (left) and cTNT (right) of differentiated cells at day 20. Bottom: Percentage of cTNT+ cells in n = 3 independent experiments. (C, G, and K) Immunostaining for cardiac Troponin T (sarcomere A band) and α-actinin A (sarcomere Z band) showed normal sarcomeric organization in patient and control lines; scale bar, 50 μm. (D, H, and L) qRT-PCR analysis of subtype-specific markers showed equal gene expression between patient and control hiPSC-derived cardiomyocytes, with the exception of SHOX2 and IRX4, which were significantly downregulated in the SHOX2 mutant c.∗28T>C line. Data are expressed as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. ∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01. Abbreviation: cTNT, cardiac Troponin T.