Figure 1.
Identification of RBPs Highly Expressed in NSCs Yet Shut Off After Neural Differentiation
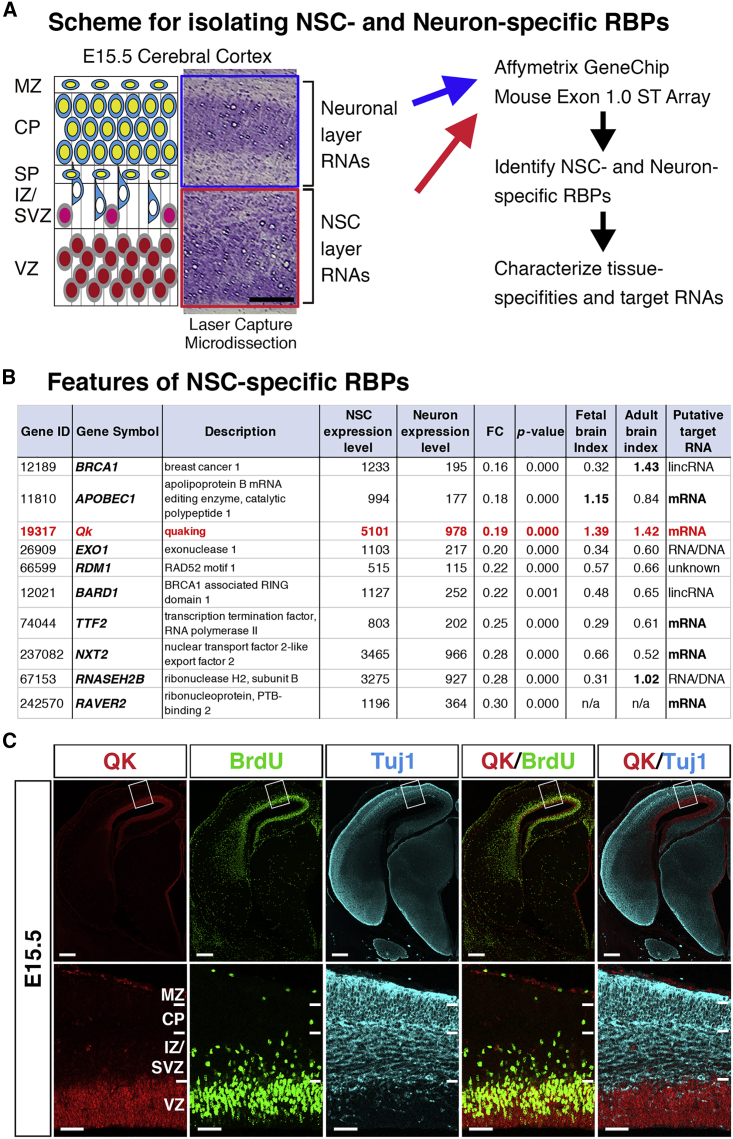
(A) Scheme for extracting RNA from NSC and neuron layers in cerebral cortices using laser capture microdissection and transcriptome analysis with ExonArray. Scale bar, 100 μm. Abbreviations: MZ, marginal zone; CP, nascent cortical plate; SP, subplate; IZ/SVZ, intermediate zone/subventricular zone; VZ, ventricular zone.
(B) Identification of NSC-specific RBPs. Mean expression levels in NSC and neuronal layers, fold change (FC) of expression levels between NSC and neuronal layers (neuron/NSC), and p values were calculated (n = 3 each for NSC and neuronal layers). Embryonic and adult brain indices were calculated based on RBP expression levels in human fetal and adult brains and compared against those of other organs (expression level in embryonic or adult brain/mean expression level in other organs) using a human RBP database that covers 1,542 RBPs (Gerstberger et al., 2014). Putative target RNAs are shown.
(C) Co-immunostaining of QK (red), BrdU (green), and Tuj1 (turquoise) in coronal sections of the cranial regions of E15.5 embryos (top). Scale bar, 250 μm. Boxed areas are shown at higher magnification in the bottom row. Scale bar, 50 μm. Abbreviations are the same as in (A).