Fig. 2.
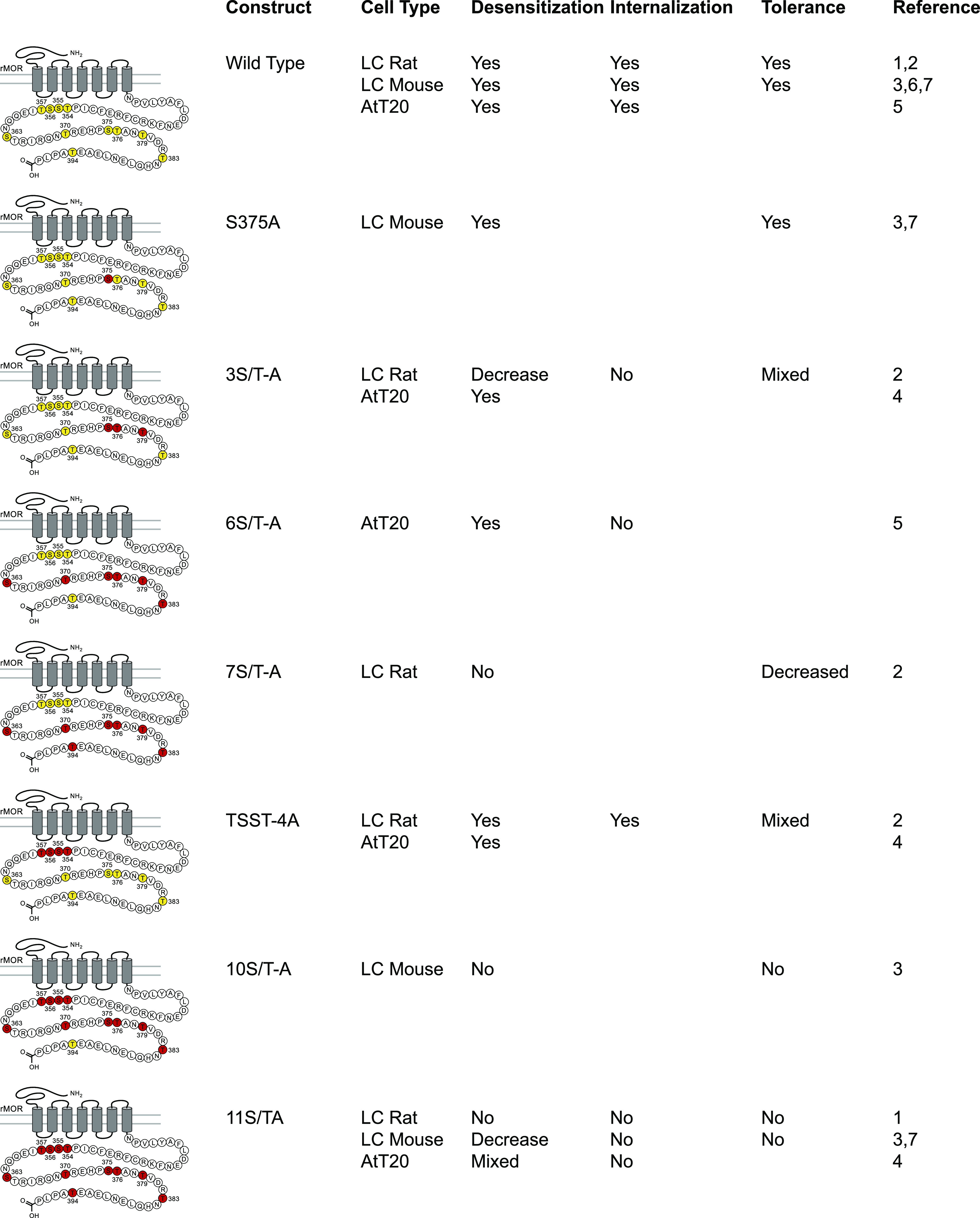
Summary of electrophysiological data examining receptor desensitization, and tolerance dependence on potential C-terminal phosphorylation sites in MOR. Eleven potential serine and threonine phosphorylation sites in the C-terminal tail of rMOR are highlighted in yellow in the wild-type rMOR (these sites are identical in rat and mouse). Potential phosphorylation sites were mutated to alanine, indicated by the red highlighting of residues, in several studies that are summarized here. These mutations are named under the Construct column. The effects of these mutations on the processes of receptor desensitization, internalization, and cellular tolerance have been measured in various systems and have been reported. Processes that remained intact in the mutant receptor are indicated with a “Yes,” whereas “No” indicates elimination of these processes, “Decreased” indicates a partial effect, and “Mixed” indicates that different assays or ligands provided differing results [sources: 1) Arttamangkul et al., 2018; 2) Arttamangkul et al., 2019b; 3) Kliewer et al., 2019; 4) Miess et al., 2018; 5) Yousuf et al., 2015; 6) Quillinan et al., 2011, 7) J. Williams, personal communication]. LC, locus coeruleus; rMOR, rat mu-opioid receptor.
